Abstract
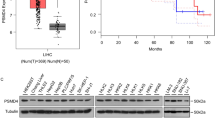
Most of the p53 target genes, all except MDM2, COP1 and PIRH2, perform functions in apoptosis, differentiation and cell cycle arrest. The aforementioned oncogenes downregulate p53 through a negative feedback mechanism, and thus contribute to tumor development. In this study, we report a new p53 target, PRL-1, which is believed to be a significant regulator in the development and metastasis of a variety of cancer types. Phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL-1) overexpression reduced the levels of endogenous and exogenous p53 proteins, and inhibited p53-mediated apoptosis. On the other hand, the ablation of PRL-1 by small interfering RNA (siRNA) increased p53 protein levels. The p53 downregulation was mediated by p53 ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. Furthermore, p53 ubiquitination by PRL-1 was achieved through two independent pathways, by inducing PIRH2 transcription and by inducing MDM2 phosphorylation through Akt signaling. In addition, we showed that the PRL-1 gene harbors a p53 response element in the first intron, and its transcription is regulated by the p53 protein. These findings imply that the new oncogenic p53 target, PRL-1, may contribute to tumor development by the downregulation of p53 by a negative feedback mechanism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achiwa H, Lazo JS . (2007). PRL-1 tyrosine phosphatase regulates c-Src levels, adherence, and invasion in human lung cancer cells. Cancer Res 67: 643–650.
Balint EE, Vousden KH . (2001). Activation and activities of the p53 tumour suppressor protein. Br J Cancer 85: 1813–1823.
Bunz F, Hwang PM, Torrance C, Waldman T, Zhang Y, Dillehay L et al. (1999). Disruption of p53 in human cancer cells alters the responses to therapeutic agents. J Clin Invest 104: 263–269.
Daoud SS, Munson PJ, Reinhold W, Young L, Prabhu VV, Yu Q et al. (2003). Impact of p53 knockout and topotecan treatment on gene expression profiles in human colon carcinoma cells: a pharmacogenomic study. Cancer Res 63: 2782–2793.
Diamond RH, Cressman DE, Laz TM, Abrams CS, Taub R . (1994). PRL-1, a unique nuclear protein tyrosine phosphatase, affects cell growth. Mol Cell Biol 14: 3752–3762.
Dornan D, Wertz I, Shimizu H, Arnott D, Frantz GD, Dowd P et al. (2004). The ubiquitin ligase COP1 is a critical negative regulator of p53. Nature 429: 86–92.
Feng J, Tamaskovic R, Yang Z, Brazil DP, Merlo A, Hess D et al. (2004). Stabilization of Mdm2 via decreased ubiquitination is mediated by protein kinase B/Akt-dependent phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 279: 35510–35517.
Fiordalisi JJ, Keller PJ, Cox AD . (2006). PRL tyrosine phosphatases regulate rho family GTPases to promote invasion and motility. Cancer Res 66: 3153–3161.
Gashler A, Sukhatme VP . (1995). Early growth response protein 1 (Egr-1): prototype of a zinc-finger family of transcription factors. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 50: 191–224.
Gius D, Cao XM, Rauscher III FJ, Cohen DR, Curran T, Sukhatme VP . (1990). Transcriptional activation and repression by Fos are independent functions: the C terminus represses immediate-early gene expression via CArG elements. Mol Cell Biol 10: 4243–4255.
Huang J, Logsdon N, Schmieg FI, Simmons DT . (1998). p53-mediated transcription induces resistance of DNA to UV inactivation. Oncogene 17: 401–411.
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Park HU, Brady JN . (2005). Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 24: 6719–6728.
Jung H, Seong HA, Ha H . (2007). NM23-H1 tumor suppressor and its interacting partner STRAP activate p53 function. J Biol Chem 282: 35293–35307.
Kim SB, Chae GW, Lee J, Park J, Tak H, Chung JH et al. (2007). Activated Notch1 interacts with p53 to inhibit its phosphorylation and transactivation. Cell Death Differ 14: 982–991.
Kobayashi D, Yamada M, Kamagata C, Kaneko R, Tsuji N, Nakamura M et al. (2002). Overexpression of early growth response-1 as a metastasis-regulatory factor in gastric cancer. Anticancer Res 22: 3963–3970.
Leng RP, Lin Y, Ma W, Wu H, Lemmers B, Chung S et al. (2003). Pirh2, a p53-induced ubiquitin–protein ligase, promotes p53 degradation. Cell 112: 779–791.
Li M, Brooks CL, Wu-Baer F, Chen D, Baer R, Gu W . (2003). Mono- versus polyubiquitination: differential control of p53 fate by Mdm2. Science 302: 1972–1975.
Liang F, Liang J, Wang WQ, Sun JP, Udho E, Zhang ZY . (2007). PRL3 promotes cell invasion and proliferation by down-regulation of Csk leading to Src activation. J Biol Chem 282: 5413–5419.
McMahon SB, Monroe JG . (1996). The role of early growth response gene 1 (egr-1) in regulation of the immune response. J Leukoc Biol 60: 159–166.
Milne D, Kampanis P, Nicol S, Dias S, Campbell DG, Fuller-Pace F et al. (2004). A novel site of AKT-mediated phosphorylation in the human MDM2 onco-protein. FEBS Lett 577: 270–276.
Miskad UA, Semba S, Kato H, Yokozaki H . (2004). Expression of PRL-3 phosphatase in human gastric carcinomas: close correlation with invasion and metastasis. Pathobiology 71: 176–184.
Nair P, Muthukkumar S, Sells SF, Han SS, Sukhatme VP, Rangnekar VM . (1997). Early growth response-1-dependent apoptosis is mediated by p53. J Biol Chem 272: 20131–20138.
Parker BS, Argani P, Cook BP, Liangfeng H, Chartrand SD, Zhang M et al. (2004). Alterations in vascular gene expression in invasive breast carcinoma. Cancer Res 64: 7857–7866.
Qureshi SA, Rim M, Bruder J, Kolch W, Rapp U, Sukhatme VP et al. (1991). An inhibitory mutant of c-Raf-1 blocks v-Src-induced activation of the Egr-1 promoter. J Biol Chem 266: 20594–20597.
Resnick-Silverman L, St Clair S, Maurer M, Zhao K, Manfredi JJ . (1998). Identification of a novel class of genomic DNA-binding sites suggests a mechanism for selectivity in target gene activation by the tumor suppressor protein p53. Genes Dev 12: 2102–2107.
Saha S, Bardelli A, Buckhaults P, Velculescu VE, Rago C, St Croix B et al. (2001). A phosphatase associated with metastasis of colorectal cancer. Science 294: 1343–1346.
Seong HA, Jung H, Ha H . (2007). NM23-H1 tumor suppressor physically interacts with serine-threonine kinase receptor-associated protein, a transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) receptor-interacting protein, and negatively regulates TGF-beta signaling. J Biol Chem 282: 12075–12096.
Song MS, Song SJ, Ayad NG, Chang JS, Lee JH, Hong HK et al. (2004). The tumour suppressor RASSF1A regulates mitosis by inhibiting the APC-Cdc20 complex. Nat Cell Biol 6: 129–137.
Stephens BJ, Han H, Gokhale V, Von Hoff DD . (2005). PRL phosphatases as potential molecular targets in cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 4: 1653–1661.
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang JP, Zeng Q . (2007). PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals through PI3K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 67: 2922–2926.
Wang Q, Holmes DI, Powell SM, Lu QL, Waxman J . (2002). Analysis of stromal–epithelial interactions in prostate cancer identifies PTPCAAX2 as a potential oncogene. Cancer Lett 175: 63–69.
Weizer-Stern O, Adamsky K, Margalit O, Ashur-Fabian O, Givol D, Amariglio N et al. (2007). Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron metabolism, is transcriptionally activated by p53. Br J Haematol 138: 253–262.
Werner SR, Lee PA, DeCamp MW, Crowell DN, Randall SK, Crowell PL . (2003). Enhanced cell cycle progression and down regulation of p21(Cip1/Waf1) by PRL tyrosine phosphatases. Cancer Lett 202: 201–211.
Westfall MD, Mays DJ, Sniezek JC, Pietenpol JA . (2003). The Delta Np63 alpha phosphoprotein binds the p21 and 14-3-3 sigma promoters in vivo and has transcriptional repressor activity that is reduced by Hay–Wells syndrome-derived mutations. Mol Cell Biol 23: 2264–2276.
Wu X, Zeng H, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Sha H, Ge X et al. (2004). Phosphatase of regenerating liver-3 promotes motility and metastasis of mouse melanoma cells. Am J Pathol 164: 2039–2054.
Yoo YG, Lee MO . (2004). Hepatitis B virus X protein induces expression of Fas ligand gene through enhancing transcriptional activity of early growth response factor. J Biol Chem 279: 36242–36249.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr Sung Hyun Kang and Dr Kwang Hee Bae (KRIBB) for providing the FLAG-PRL-1. This work was supported by funding from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Korea (M1040101001-06N0101-00110).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Min, SH., Kim, D., Heo, YS. et al. New p53 target, phosphatase of regenerating liver 1 (PRL-1) downregulates p53. Oncogene 28, 545–554 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.409
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.409
- Springer Nature Limited
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Functional loss of p53 cooperates with the in vivo microenvironment to promote malignant progression of gastric cancers
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Census and evaluation of p53 target genes
Oncogene (2017)
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases as potential therapeutic targets
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2014)
-
Gene expression profiling of peripheral blood mononuclear cells in the setting of peripheral arterial disease
Journal of Clinical Bioinformatics (2012)
-
Metastasis-associated phosphatase PRL-2 regulates tumor cell migration and invasion
Oncogene (2012)