Abstract
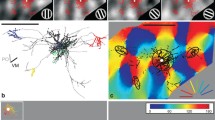
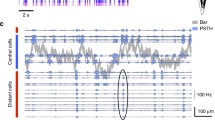
Different streams of sensory information are transmitted to the cortex where they are merged into a percept in a process often termed 'binding.' Using recordings from triplets of rat cortical layer 2/3 and layer 5 pyramidal neurons, we show that specific subnetworks within layer 5 receive input from different layer 2/3 subnetworks. This cortical microarchitecture may represent a mechanism that enables the main output of the cortex (layer 5) to bind different features of a sensory stimulus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hubel, D.H. & Wiesel, T.N. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 160, 106–154 (1962).
Mountcastle, V.B. J. Neurophysiol. 20, 408–434 (1957).
Song, S., Sjostrom, P.J., Reigl, M., Nelson, S. & Chklovskii, D.B. PLoS Biol. [online] 3, e68 (2005) (doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0030068).
Wang, Y. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 534–542 (2006).
Yoshimura, Y., Dantzker, J.L. & Callaway, E.M. Nature 433, 868–873 (2005).
Shepherd, G.M. & Svoboda, K. J. Neurosci. 25, 5670–5679 (2005).
Bosking, W.H., Zhang, Y., Schofield, B. & Fitzpatrick, D. J. Neurosci. 17, 2112–2127 (1997).
Marino, J. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 194–201 (2005).
Sincich, L.C. & Blasdel, G.G. J. Neurosci. 21, 4416–4426 (2001).
Weliky, M., Kandler, K., Fitzpatrick, D. & Katz, L.C. Neuron 15, 541–552 (1995).
Berman, N., Payne, B.R., Labar, D.R. & Murphy, E.H. J. Neurophysiol. 48, 1362–1377 (1982).
Martinez, L.M. et al. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 372–379 (2005).
Williams, S.R. & Stuart, G.J. Science 295, 1907–1910 (2002).
Kampa, B.M., Letzkus, J.J. & Stuart, G.J. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 574, 283–290 (2006).
Letzkus, J.J., Kampa, B.M. & Stuart, G.J. J. Neurosci. 26, 10420–10429 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Stricker and J. Bekkers for help with the analysis and F. Helmchen, C. Gee and W. Schweer for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.M.K. designed the experiments and did the calculations; B.M.K. and J.J.L. performed the experiments and data analysis; B.M.K., J.J.L. and G.J.S. jointly discussed the results and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figure 1
Integrative feed-forward networks in the neocortex. (PDF 41 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kampa, B., Letzkus, J. & Stuart, G. Cortical feed-forward networks for binding different streams of sensory information. Nat Neurosci 9, 1472–1473 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1798
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1798
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Immediate reuse of patch-clamp pipettes after ultrasonic cleaning
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Graphene-electrode array for brain map remodeling of the cortical surface
NPG Asia Materials (2021)
-
Divergent Projection Patterns Revealed by Reconstruction of Individual Neurons in Orbitofrontal Cortex
Neuroscience Bulletin (2021)
-
Anatomy and function of an excitatory network in the visual cortex
Nature (2016)
-
Multilaminar networks of cortical neurons integrate common inputs from sensory thalamus
Nature Neuroscience (2016)