Abstract
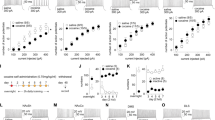
The core and shell of the nucleus accumbens have critical, differential roles in drug-dependent behaviors. Here we show that operant cocaine self-administration inhibits long-term depression (LTD) in both structures after 1 d of abstinence. However, after 21 d of abstinence, LTD was abolished exclusively in the nucleus accumbens core of cocaine self-administering rats, suggesting that voluntary cocaine self-administration induced long-lasting neuroadaptations in the core that could underlie drug-seeking behavior and relapse.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shaham, Y. & Hope, B.T. Nat. Neurosci. 8, 1437–1439 (2005).
Kalivas, P.W., Volkow, N. & Seamans, J. Neuron 45, 647–650 (2005).
Kelley, A.E. Neuron 44, 161–179 (2004).
Kalivas, P.W. & McFarland, K. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 168, 44–56 (2003).
Cardinal, R.N., Parkinson, J.A., Hall, J. & Everitt, B.J. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 26, 321–352 (2002).
Pierce, R.C. & Kumaresan, V. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 30, 215–238 (2006).
Rebec, G.V., Christensen, J.R., Guerra, C. & Bardo, M.T. Brain Res. 776, 61–67 (1997).
Thomas, M.J., Beurrier, C., Bonci, A. & Malenka, R.C. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1217–1223 (2001).
Ungless, M.A., Whistler, J.L., Malenka, R.C. & Bonci, A. Nature 411, 583–587 (2001).
Boudreau, A.C. & Wolf, M.E. J. Neurosci. 25, 9144–9151 (2005).
Brebner, K. et al. Science 310, 1340–1343 (2005).
Sutton, M.A. et al. Nature 421, 70–75 (2003).
Gerdeman, G.L., Partridge, J.G., Lupica, C.R. & Lovinger, D.M. Trends Neurosci. 26, 184–192 (2003).
Udo, T., Ugalde, F., DiPietro, N., Eichenbaum, H.B. & Kantak, K.M. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 174, 237–245 (2004).
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders 4th edn. (American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC, 2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank L. Daitch for editorial assistance. This work was supported by funds from the State of California for medical research on alcohol and substance abuse through the University of California, San Francisco (A.B.) and the National Institutes of Health 1RO1DA15096-01 (A.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.M., B.T.C. and F.W.H. contributed toward the electrophysiological experiments. M.M., B.T.C. and M.S.B. contributed toward animal training.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, M., Chen, B., Hopf, F. et al. Cocaine self-administration selectively abolishes LTD in the core of the nucleus accumbens. Nat Neurosci 9, 868–869 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1713
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1713
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Cocaine-induced loss of LTD and social impairments are restored by fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibition
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Food for thought: diet-induced impairments to decision-making and amelioration by N-acetylcysteine in male rats
Psychopharmacology (2022)
-
Drug addiction: from bench to bedside
Translational Psychiatry (2021)
-
Effects of ketamine treatment on cocaine-induced reinstatement and disruption of functional connectivity in unanesthetized rhesus monkeys
Psychopharmacology (2019)
-
Dopamine and addiction: what have we learned from 40 years of research
Journal of Neural Transmission (2019)