Abstract
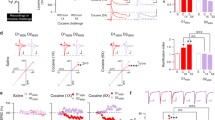
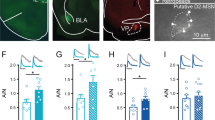
The neural mechanism underlying the relapse to drug use after drug withdrawal is largely unknown. We found that after withdrawal from repeated cocaine exposure, excitatory synapses onto dopamine neurons in the ventral tegmental area (VTA) of the rat midbrain became highly susceptible to potentiation by weak presynaptic stimuli, an effect requiring endogenous brain-derived neurotrophic factor–tyrosine kinase B (BDNF-TrkB) signaling. The elevated BDNF expression in the VTA after cocaine withdrawal may prime these synapses for potentiation by cue-associated activity, triggering drug craving and relapse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nestler, E.J. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 119–128 (2001).
Hyman, S.E. & Malenka, R.C. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 695–703 (2001).
Kauer, J.A. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 66, 447–475 (2004).
Ungless, M.A., Whistler, J.L., Malenka, R.C. & Bonci, A. Nature 411, 583–587 (2001).
Liu, Q.S., Pu, L. & Poo, M.M. Nature 437, 1027–1031 (2005).
Grimm, J.W. et al. J. Neurosci. 23, 742–747 (2003).
Boulanger, L. & Poo, M.M. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 346–351 (1999).
Figurov, A., Pozzo-Miller, L.D., Olafsson, P., Wang, T. & Lu, B. Nature 381, 706–709 (1996).
Poo, M.M. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 24–32 (2001).
Watanabe, S., Hoffman, D.A., Migliore, M. & Johnston, D. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 8366–8371 (2002).
Wolf, M.E. Prog. Neurobiol. 54, 679–720 (1998).
Bekkers, J.M. & Stevens, C.F. Nature 346, 724–729 (1990).
McClung, C.A. & Nestler, E.J. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 1208–1215 (2003).
Horger, B.A. et al. J. Neurosci. 19, 4110–4122 (1999).
Lu, L., Dempsey, J., Liu, S.Y., Bossert, J.M. & Shaham, Y. J. Neurosci. 24, 1604–1611 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank C.C. Lien, J.L. Du, Z.R. Wang and L. Cancedda for critical comments and suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Electrophysiological identification of dopamine neurons. (PDF 357 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Enhanced LTP in rats examined 10-15 d after cocaine withdrawal. (PDF 117 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Bath perfusion of BDNF sensitized the excitatory synapses on dopamine neurons for synaptic potentiation by weak presynaptic stimulation (WPS). (PDF 79 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, L., Liu, Qs. & Poo, Mm. BDNF-dependent synaptic sensitization in midbrain dopamine neurons after cocaine withdrawal. Nat Neurosci 9, 605–607 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1687
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1687
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Peripheral neurotrophin levels during controlled crack/cocaine abstinence: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Reinstatement of nicotine conditioned place preference in a transgenerational model of drug abuse vulnerability in psychosis: Impact of BDNF on the saliency of drug associations
Psychopharmacology (2023)
-
Effects of Compound 511 on BDNF-TrkB Signaling in the Mice Ventral Tegmental Area in Morphine-Induced Conditioned Place Preference
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
-
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Nucleus Accumbens Mediates Individual Differences in Behavioral Responses to a Natural, Social Reward
Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
Different doses of methamphetamine alter long-term potentiation, level of BDNF and neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus of reinstated rats
The Journal of Physiological Sciences (2019)