Abstract
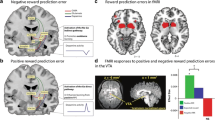
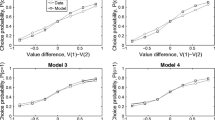
Previous work has shown that human adolescents may be hypersensitive to rewards, but it is not known which aspect of reward processing is responsible for this. We separated decision value and prediction error signals and found that neural prediction error signals in the striatum peaked in adolescence, whereas neural decision value signals varied depending on how value was modeled. This suggests that heightened dopaminergic prediction error responsivity contributes to adolescent reward seeking.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Casey, B.J., Getz, S. & Galvan, A. Dev. Rev. 28, 62–77 (2008).
Kahneman, D. & Tversky, A. Econometrica 47, 263–291 (1979).
Chib, V.S., Rangel, A., Shimojo, S. & O'Doherty, J.P. J. Neurosci. 29, 12315–12320 (2009).
Tom, S.M., Fox, C.R., Trepel, C. & Poldrack, R.A. Science 315, 515–518 (2007).
Rescorla, R.A. & Wagner, A.R. in Classical Conditioning II: Current Research and Theory (eds. Black, A. & Prokasy, W.F.) 64–99 (Appleton Century Crofts, New York, 1972).
Schultz, W., Dayan, P. & Montague, P.R. Science 275, 1593–1599 (1997).
Pagnoni, G., Zink, C.F., Montague, P.R. & Berns, G.S. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 97–98 (2002).
Ernst, M. et al. Neuroimage 25, 1279–1291 (2005).
Galvan, A. et al. J. Neurosci. 26, 6885–6892 (2006).
Bjork, J.M. et al. J. Neurosci. 24, 1793–1802 (2004).
May, J.C. et al. Biol. Psychiatry 55, 359–366 (2004).
Knowlton, B.J., Mangels, J.A. & Squire, L.R. Science 273, 1399–1402 (1996).
Hare, T.A., O'Doherty, J., Camerer, C.F., Schultz, W. & Rangel, A. J. Neurosci. 28, 5623–5630 (2008).
D'Ardenne, K., McClure, S.M., Nystrom, L.E. & Cohen, J.D. Science 319, 1264–1267 (2008).
Berridge, K.C. & Robinson, T.E. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 28, 309–369 (1998).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (5R24 MH072697), the National Institute of Drug Abuse (5F31 DA024534), the James S. McDonnell Foundation and the Della Martin Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.R.C. helped design the experiments, conducted data acquisition and analyses, and wrote the manuscript. R.F.A., R.M.B. and S.Y.B. designed the experiments. F.W.S. contributed to data acquisition. B.J.K. and R.A.P. designed the experiments and helped write the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9, Supplementary Tables 1–5 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 3051 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, J., Asarnow, R., Sabb, F. et al. A unique adolescent response to reward prediction errors. Nat Neurosci 13, 669–671 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2558
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2558
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Goal-directed learning in adolescence: neurocognitive development and contextual influences
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2024)
-
Impaired learning to dissociate advantageous and disadvantageous risky choices in adolescents
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A methodological perspective on learning in the developing brain
npj Science of Learning (2022)
-
Decision-making and cognitive control in adolescent suicidal behaviors: a qualitative systematic review of the literature
European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry (2021)
-
The rational use of causal inference to guide reinforcement learning strengthens with age
npj Science of Learning (2020)