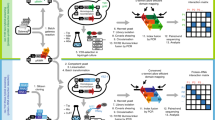
Abstract
Present screening methods for protein-protein interactions (PPIs) rely on the overexpression of artificial fusion proteins, making it difficult to assess in vivo relevance. Here we combine stable isotope labeling with amino acids in cell culture (SILAC), RNA interference (RNAi), coimmunoprecipitation and quantitative mass-spectrometry analysis to detect cellular interaction partners of endogenous proteins in mammalian cells with very high confidence. We used this screen to identify interaction partners of β-catenin and Cbl.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bader, J.S., Chaudhuri, A., Rothberg, J.M. & Chant, J. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 78–85 (2004).
Li, S. et al. Science 303, 540–543 (2004).
Zhu, H., Bilgin, M. & Snyder, M. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 783–812 (2003).
Aebersold, R. & Mann, M. Nature 422, 198–207 (2003).
Ong, S.E. & Mann, M. Nat. Chem. Biol. 1, 252–262 (2005).
Ong, S.E. et al. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 376–386 (2002).
Schulze, W.X. & Mann, M. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 10756–10764 (2004).
Gunsalus, K.C. & Piano, F. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 17, 3–8 (2005).
Reya, T. & Clevers, H. Nature 434, 843–850 (2005).
van de Wetering, M. et al. EMBO Rep. 4, 609–615 (2003).
Kucerova, D., Sloncova, E., Tuhackova, Z., Vojtechova, M. & Sovova, V. Int. J. Mol. Med. 8, 695–698 (2001).
Kim, I.J. et al. Clin. Cancer Res. 9, 2920–2925 (2003).
Schmidt, M.H. & Dikic, I. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 907–919 (2005).
Silva, J.M. et al. Nat. Genet. 37, 1281–1288 (2005).
Uhlen, M. et al. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 4, 1920–1932 (2005).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Blagoev from the Center of Experimental Bioinformatics for fruitful discussions, J.V. Olsen and other members of our department for discussion and assistance, H. Clevers for generously providing us with the inducible β-catenin knockdown cell line and the Interaction Proteome project of the European Union for funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Table 1
Sequences and normalized abundance ratios of the quantified peptides for β-catenin and three detected interaction partners. (DOC 38 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Sequences and normalized abundance ratios of the quantified peptides for Cbl and four detected interaction partners. (DOC 39 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Additional proteins identified with increased abundance ratios in the Cbl pulldown. (DOC 40 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
Ratio of proteins identified in the whole cell lysates after Cbl knock-down. (DOC 201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selbach, M., Mann, M. Protein interaction screening by quantitative immunoprecipitation combined with knockdown (QUICK). Nat Methods 3, 981–983 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth972
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth972
- Springer Nature America, Inc.