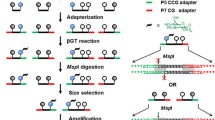
Abstract
We describe strand-specific, base-resolution detection of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) in genomic DNA with single-molecule sensitivity, combining a bioorthogonal, selective chemical labeling method of 5-hmC with single-molecule, real-time (SMRT) DNA sequencing. The chemical labeling not only allows affinity enrichment of 5-hmC–containing DNA fragments but also enhances the kinetic signal of 5-hmC during SMRT sequencing. We applied the approach to sequence 5-hmC in a genomic DNA sample with high confidence.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kriaucionis, S. & Heintz, N. Science 324, 929–930 (2009).
Tahiliani, M. et al. Science 324, 930–935 (2009).
Bhutani, N., Burns, D.M. & Blau, H.M. Cell 146, 866–872 (2011).
Huang, Y. et al. PLoS ONE 5, e8888 (2010).
Song, C.X. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 68–72 (2011).
Wu, H. et al. Genes Dev. 25, 679–684 (2011).
Ficz, G. et al. Nature 473, 398–402 (2011).
Pastor, W.A. et al. Nature 473, 394–397 (2011).
Williams, K. et al. Nature 473, 343–348 (2011).
Xu, Y. et al. Mol. Cell 42, 451–464 (2011).
Munzel, M., Globisch, D. & Carell, T. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 6460–6468 (2011).
Eid, J. et al. Science 323, 133–138 (2009).
Flusberg, B.A. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 461–465 (2010).
Travers, K.J., Chin, C.S., Rank, D.R., Eid, J.S. & Turner, S.W. Nucleic Acids Res. 38, e159 (2010).
Korlach, J. et al. Methods Enzymol. 472, 431–455 (2010).
Dai, Q., Song, C.X., Pan, T. & He, C. J. Org. Chem. 76, 4182–4188 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported partly by US National Institutes of Health grants GM071440 (to C.H.) and 1RC2HG005618-01 (National Human Genome Research Institute to S.T.) and The University of Chicago. We thank K. Spittle, M. Boitano, J. Eid, J. Wegener and K. Luong for assistance in data acquisition and figure generation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.H., C.-X.S., J.K. and S.W.T. designed experiments. C.-X.S. performed the labeling and pulldown of synthetic template and mESC sample. T.A.C. prepared library constructs and conducted the sequencing experiments. A.K. analyzed data. Q.D., C.-X.S. and X.-Y.L. carried out the chemical synthesis. X.-Y.L. validated mESC hits. C.H., C.-X.S. and J.K. wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
T.A.C., S.W.T. and J.K. are employees of Pacific Biosciences, which commercializes single-molecule, real-time sequencing technologies.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–3 and Supplementary Tables 1–3 (PDF 1749 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, CX., Clark, T., Lu, XY. et al. Sensitive and specific single-molecule sequencing of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine. Nat Methods 9, 75–77 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1779
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1779
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Bisulfite-free mapping of DNA cytosine modifications: challenges and perspectives
Science China Chemistry (2023)
-
Tissue-specific 5-hydroxymethylcytosine landscape of the human genome
Nature Communications (2021)
-
TETology: Epigenetic Mastermind in Action
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2021)
-
Ten-eleven translocation protein 1 modulates medulloblastoma progression
Genome Biology (2021)
-
Photoelectrochemical assay for DNA hydroxymethylation determination based on the inhibited photoactivity of black TiO2 nanosphere by ZnO
Microchimica Acta (2020)