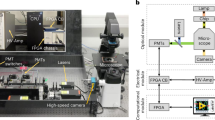
Abstract
A parallel microfluidic cytometer (PMC) uses a high-speed scanning photomultiplier-based detector to combine low-pixel-count, one-dimensional imaging with flow cytometry. The 384 parallel flow channels of the PMC decouple count rate from signal-to-noise ratio. Using six-pixel one-dimensional images, we investigated protein localization in a yeast model for human protein misfolding diseases and demonstrated the feasibility of a nuclear-translocation assay in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing an NFκB-EGFP reporter.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Taylor, D.L., Haskins, J.R. & Giuliano, K.A. High Content Screening (Humana Press, 2007).
De Vos, W.H., Van Neste, L., Dieriks, B., Joss, G.H. & Van Oostveldt, P. Cytometry A 77A, 64–75 (2010).
Perlman, Z.E. et al. Science 306, 1194–1198 (2004).
Ng, A.Y.J. et al. J. Biomol. Screen 15, 858–868 (2010).
Comeau, J.W.D., Costantino, S. & Wiseman, P.W. Biophys. J. 91, 4611–4622 (2006).
Lapan, P. et al. PLoS 4, e6822 (2009).
Feng, Y., Bender, T.J., Young, D.W. & Tallarico, J.A. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 8, 567–578 (2009).
George, T.C., Fanning, S.L., Fitzgerald-Bocarsly, P. & Medeiros, R.B. J. Immunol. Methods 311, 117–129 (2006).
McKenna, B.K., Salim, H., Bringhurst, F.R. & Ehrlich, D.J. Lab Chip 9, 305–310 (2009).
Krishnan, R. & Lindquist, S.L. Nature 435, 765–772 (2005).
Shorter, J. & Lindquist, S.L. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6, 435–450 (2005).
Ding, G.J. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28897–28905 (1998).
Schmid, J.A., Birbach, A. & Hofer-Warbinek, R. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 17035–17042 (2000).
Bohm, S., Gilbert, J. & Deshpande, M. US patent 7,157,274 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Bevis and S. Lindquist (Whitehead Institute) for helpful conversations and for supplying the S. cerevisiae samples. This work was supported by US National Institutes of Health (grant R01 HG-001389).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
B.K.M., J.G.E., M.C.C. and D.J.E. designed the research; B.K.M., M.C.C., J.G.E. and D.J.E. performed the engineering and experiments; B.K.M. and M.C.C. wrote analytical software and performed the data analysis; and all authors contributed to writing the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–14, Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 4763 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKenna, B., Evans, J., Cheung, M. et al. A parallel microfluidic flow cytometer for high-content screening. Nat Methods 8, 401–403 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1595
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1595
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
A review of microscopic cell imaging and neural network recognition for synergistic cyanobacteria identification and enumeration
Analytical Sciences (2022)
-
Multiplex Immunoassays Utilizing Differential Affinity Using Aptamers Generated by MARAS
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
In vitro acute and developmental neurotoxicity screening: an overview of cellular platforms and high-throughput technical possibilities
Archives of Toxicology (2017)
-
Distribution Analyzer, a methodology for identifying and clustering outlier conditions from single-cell distributions, and its application to a Nanog reporter RNAi screen
BMC Bioinformatics (2015)
-
Imaging Cells in Flow Cytometer Using Spatial-Temporal Transformation
Scientific Reports (2015)