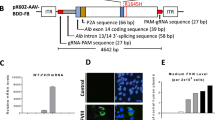
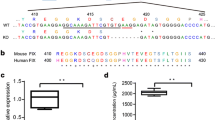
Abstract
Conventional gene therapy of hemophilia A relies on the transfer of factor VIII (FVIII; encoded by the F8 gene) cDNA. We carried out spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing (SMaRT) to repair mutant FVIII mRNA. A pre-trans-splicing molecule (PTM) corrected endogenous FVIII mRNA in F8 knockout mice with the hemophilia A phenotype, producing sufficient functional FVIII to correct the hemophilia A phenotype. This is the first description of phenotypic correction of a genetic defect by RNA repair in a knockout animal model. Our results indicate the feasibility of using SMaRT to repair RNA for the treatment of genetic diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaufman, R.J. & Antonarakis, S.E. Structure, biology, and genetics of factor VIII. in Hematology: Basic Principles and Practice Vol. VIII-108 (ed. McGlave, P.) 1850–1868 (Church Livingstone, New York, 2000).
Lillicrap, D. Hemophilia treatment. Gene therapy, factor VIII antibodies and immune tolerance: hopes and concerns. Haematologica 85, 108–111 (2000).
Bi, L. et al. Targeted disruption of the mouse factor VIII gene produces a model of haemophilia A. Nat. Genet. 10, 119–121 (1995).
Bi, L. et al. Further characterization of factor VIII-deficient mice created by gene targeting: RNA and protein studies. Blood 88, 3446–3450 (1996).
Sullenger, B.A. & Cech, T.R. Ribozyme-mediated repair of defective mRNA by targeted, trans-splicing. Nature 371, 619–622 (1994).
Sullenger, B.A. RNA repair as a novel approach to genetic therapy. Gene Ther. 6, 461–462 (1999).
Watanabe, T. & Sullenger, B.A. RNA repair: a novel approach to gene therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 44, 109–118 (2000).
Gorman, L., Mercatante, D. & Kole, R. Restoration of correct splicing of thalassemic beta-globin pre-mRNA by modified U1 snRNAs. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35914–35919 (2000).
Puttaraju, M., Jamison, S.F., Mansfield, S.G., Garcia-Blanco, M.A. & Mitchell, L.G. Spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing as a tool for gene therapy. Nat. Biotechnol. 17, 246–452 (1999).
Puttaraju, M., DiPasquale, J., Baker, C.C., Mitchell, L.G. & Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Messenger RNA repair and restoration of protein function by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Mol. Ther. 4, 105–114 (2001).
Mansfield, S.G. et al. Repair of CFTR mRNA by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Gene Ther. 7, 1885–1895 (2000).
Liu, X. et al. Partial correction of endogenous DeltaF508 CFTR in human cystic fibrosis airway epithelia by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Nat. Biotechnol. 20, 47–52 (2002).
Roy, S. et al. In vivo evaluation of a novel epitope-tagged human factor VIII-encoding adenoviral vector. Haemophilia 5, 340–348 (1999).
Budker, V., Zhang, G., Knechtle, S. & Wolff, J. Naked DNA delivered intraportally expresses efficiently in hepatocytes. Gene Ther. 3, 593–598 (1996).
Yenchitsomanus, P. et al. Mutation causing exon 15 skipping and partial exon 16 deletion in factor VIII transcript, and a method for direct mutation detection. Haemophilia 7, 335–338 (2001).
Herweijer, H. et al. Time course of gene expression after plasmid DNA gene transfer to the liver. J. Gene. Med. 3, 280–291 (2001).
Koehler, D.R., Hitt, M.M. & Hu, J. Challenges and strategies for cystic fibrosis lung gene therapy. Mol. Ther. 4, 84–91 (2001).
Karpati, G. & Acsadi, G. The principles of gene therapy in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Clin. Invest. Med. 17, 499–509 (1994).
Kikumori, T., Cote, G.J. & Gagel, R.F. Promiscuity of pre-mRNA spliceosome-mediated trans splicing: a problem for gene therapy? Hum. Gene Ther. 12, 1429–1441 (2001).
He, T. et al. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2509–2514 (1998).
Chao, H., Monahan, P., Liu, Y., Samulski, R. & Walsh, C. Sustained and complete phenotype correction of hemophilia B mice following intramuscular injection of AAV1 serotype vectors. Mol. Ther. 4, 217–222 (2001).
Chao, H., Mao, L., Bruce, A. & Walsh, C. Sustained expression of human factor VIII in mice using a parvovirus-based vector. Blood 95, 1594–1599 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Huang and X. Zeng for technical assistance, S. Connelly and P. Shirley (GTI/Novartis) for the AdhuF8 mouse plasma and R. Sarkar and H. Kazazian for the F8 E16 knockout mice and advice. H.J.C. is a recipient of a Career Development Award from the National Hemophilia Foundation. National Institutes of Health grant RO1-68215 provided funding for this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
S.G.M., R.C.B., S.H. and L.G.M. are employees of Intronn Inc. M.A.G.-B. is a consultant of Intronn Inc.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, H., Mansfield, S., Bartel, R. et al. Phenotype correction of hemophilia A mice by spliceosome-mediated RNA trans-splicing. Nat Med 9, 1015–1019 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm900
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm900
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Splicing mutations in the CFTR gene as therapeutic targets
Gene Therapy (2022)
-
Reprogramming the Dynamin 2 mRNA by Spliceosome-mediated RNA Trans-splicing
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2016)
-
Lessons from non-canonical splicing
Nature Reviews Genetics (2016)
-
Construction and validation of an RNA trans-splicing molecule suitable to repair a large number of COL7A1 mutations
Gene Therapy (2016)
-
Repair of Rhodopsin mRNA by Spliceosome-Mediated RNA Trans -Splicing: A New Approach for Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa
Molecular Therapy (2015)