Abstract
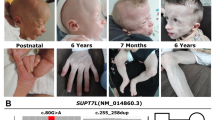
Warburg Micro syndrome (WARBM1) is a severe autosomal recessive disorder characterized by developmental abnormalities of the eye and central nervous system and by microgenitalia. We identified homozygous inactivating mutations in RAB3GAP, encoding RAB3 GTPase activating protein, a key regulator of the Rab3 pathway implicated in exocytic release of neurotransmitters and hormones, in 12 families with Micro syndrome. We hypothesize that the underlying pathogenesis of Micro syndrome is a failure of exocytic release of ocular and neurodevelopmental trophic factors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Warburg, M. et al. Am. J. Dis. Child 147, 1309–1312 (1993).
Ainsworth, J.R. et al. Ophthalmology 108, 491–497 (2001).
Graham, J.M. Jr. et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. 128A, 235–245 (2004).
Megarbane, A. et al. J. Med. Genet. 36, 637–640 (1999).
Fukui, K. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4655–4658 (1997).
Nagano, F. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24781–24785 (1998).
Takai, Y. et al. Physiol. Rev. 81, 153–208 (2001).
Zerial, M. & McBride, H. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 107–117 (2001).
Li, L. & Chin, L.S. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 60, 942–960 (2003).
Sudhof, T.C. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 509–547 (2004).
Schluter, O.M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40919–40929 (2002).
Hiesinger, P.R. et al. J. Neurosci. 19, 7548–7556 (1999).
Owens, D.F. & Kriegstein, A.R. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 715–727 (2002).
Jelitai, M. et al. J. Neurosci. Res. 76, 801–811 (2004).
Di, G.G. et al. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 150, 17–22 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank the families who helped with this research; many colleagues, particularly E.R. Roeder and C.J. Curry, for referring affected individuals; and the UK Birth Defects Foundation, the Wellcome Trust and Birmingham Women's Hospital R&D Fund for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Expression of RAB3GAP/WARBM1 (Rab3-GAP p130 catalytic subunit) mRNA in the mouse embryo as assessed by in situ hybridisation. (PDF 1491 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Fine mapping data for the affected individuals from families K1–K5. (PDF 91 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Primer sequences of novel microsatellite markers used for linkage analysis. (PDF 41 kb)
Supplementary Table 3
Clinical data for the Micro families in this study not previously described in the literature. (PDF 70 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aligianis, I., Johnson, C., Gissen, P. et al. Mutations of the catalytic subunit of RAB3GAP cause Warburg Micro syndrome. Nat Genet 37, 221–224 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1517
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1517
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
The Role of Rab GTPases in the development of genetic and malignant diseases
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2024)
-
Clinical and genetic spectrums of 413 North African families with inherited retinal dystrophies and optic neuropathies
Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2022)
-
Two novel Warburg micro syndrome 1 cases caused by pathogenic variants in RAB3GAP1
Human Genome Variation (2021)
-
Global effects of RAB3GAP1 dysexpression on the proteome of mouse cortical neurons
Amino Acids (2021)
-
Rab18: new insights into the function of an essential protein
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2019)