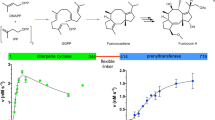
Abstract
The structure of ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase reveals three α-helical domains (α, β and γ), as also observed in the related diterpene cyclase taxadiene synthase. However, active sites are located at the interface of the βγ domains in ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase but exclusively in the α domain of taxadiene synthase. Modular domain architecture in plant diterpene cyclases enables the evolution of alternative active sites and chemical strategies for catalyzing isoprenoid cyclization reactions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tholl, D. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 9, 297–304 (2006).
Gershenzon, J. & Dudareva, N. Nat. Chem. Biol. 3, 408–414 (2007).
Bohlmann, J. & Keeling, C.I. Plant J. 54, 656–669 (2008).
Wendt, K.U. & Schulz, G.E. Structure 6, 127–133 (1998).
Wendt, K.U., Schulz, G.E., Corey, E.J. & Liu, D.R. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 39, 2812–2833 (2000).
Christianson, D.W. Chem. Rev. 106, 3412–3442 (2006).
Christianson, D.W. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 12, 141–150 (2008).
Lesburg, C.A., Zhai, G., Cane, D.E. & Christianson, D.W. Science 277, 1820–1824 (1997).
Rynkiewicz, M.J., Cane, D.E. & Christianson, D.W. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 13543–13548 (2001).
Tarshis, L.C., Yan, M., Poulter, C.D. & Sacchettini, J.C. Biochemistry 33, 10871–10877 (1994).
Cao, R. et al. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinformatics 78, 2417–2432 (2010).
Whittington, D.A. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15375–15380 (2002).
Starks, C.M., Back, K., Chappell, J. & Noel, J.P. Science 277, 1815–1820 (1997).
Wendt, K.U., Poralla, K. & Schulz, G.E. Science 277, 1811–1815 (1997).
Thoma, R. et al. Nature 432, 118–122 (2004).
Köksal, M., Jin, Y., Coates, R.M., Croteau, R. & Christianson, D.W. Nature 469, 116–120 (2011).
Prisic, S., Xu, J., Coates, R.M. & Peters, R.J. ChemBioChem 8, 869–874 (2007).
Sun, T.-P. & Kamiya, Y. Plant Cell 6, 1509–1518 (1994).
Reinert, D.J., Balliano, G. & Schulz, G.E. Chem. Biol. 11, 121–126 (2004).
Gandour, R.D. Bioorg. Chem. 10, 169–176 (1981).
Wendt, K.U., Lenhart, A. & Schulz, G.E. J. Mol. Biol. 286, 175–187 (1999).
Sato, T. & Hoshino, T. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 63, 2189–2198 (1999).
Prisic, S. & Peters, R.J. Plant Physiol. 144, 445–454 (2007).
Corey, E.J. et al. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 119, 1277–1288 (1997).
Ochs, D., Tappe, C.H., Gärtner, P., Kellner, R. & Poralla, K. Eur. J. Biochem. 194, 75–80 (1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank the US National Institutes of Health for grants GM56838 (D.W.C.), GM13956 (R.M.C.) and GM76324 (R.J.P.) for support of this research. Additionally, we thank the Advanced Photon Source at Argonne National Laboratory for beamline access.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.K. and D.W.C. performed the X-ray crystallographic studies. H.H. and R.M.C. synthesized terpenoid diphosphate ligands. R.J.P. supplied the AtCPSd84 construct, and M.K. prepared the final CPS construct that yielded crystals. All authors contributed to the interpretation of the results and preparation of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Methods and Supplementary Results (PDF 3963 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Köksal, M., Hu, H., Coates, R. et al. Structure and mechanism of the diterpene cyclase ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase. Nat Chem Biol 7, 431–433 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.578
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.578
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Structure-guided product determination of the bacterial type II diterpene synthase Tpn2
Communications Chemistry (2022)
-
Mining methods and typical structural mechanisms of terpene cyclases
Bioresources and Bioprocessing (2021)
-
A monodomain class II terpene cyclase assembles complex isoprenoid scaffolds
Nature Chemistry (2020)
-
Computer-Aided Saturation Mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana Ent-Copalyl Diphosphate Synthase
Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences (2020)
-
On the Evolution and Functional Diversity of Terpene Synthases in the Pinus Species: A Review
Journal of Molecular Evolution (2020)