Abstract
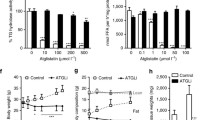
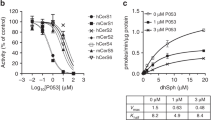
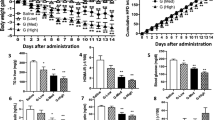
Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) is rate limiting in the mobilization of fatty acids from cellular triglyceride stores. This central role in lipolysis marks ATGL as an interesting pharmacological target as deregulated fatty acid metabolism is closely linked to dyslipidemic and metabolic disorders. Here we report on the development and characterization of a small-molecule inhibitor of ATGL. Atglistatin is selective for ATGL and reduces fatty acid mobilization in vitro and in vivo.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haemmerle, G. et al. Science 312, 734–737 (2006).
Lass, A. et al. Cell Metab. 3, 309–319 (2006).
Zimmermann, R. et al. Science 306, 1383–1386 (2004).
Fredrikson, G., Tornqvist, H. & Belfrage, P. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 876, 288–293 (1986).
Zimmermann, R., Lass, A., Haemmerle, G. & Zechner, R. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1791, 494–500 (2009).
Boden, G. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 18, 139–143 (2011).
Carobbio, S., Rodriguez-Cuenca, S. & Vidal-Puig, A. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 14, 520–526 (2011).
Schaffer, J.E. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14, 281–287 (2003).
Kienesberger, P.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 284, 30218–30229 (2009).
Hoy, A.J. et al. Endocrinology 152, 48–58 (2011).
Ong, K.T., Mashek, M.T., Bu, S. & Mashek, D.G. FASEB J. 27, 313–321 (2013).
Li, L.O., Klett, E.L. & Coleman, R.A. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1801, 246–251 (2010).
Summers, S.A. Prog. Lipid Res. 45, 42–72 (2006).
Samuel, V.T., Petersen, K.F. & Shulman, G.I. Lancet 375, 2267–2277 (2010).
Ebdrup, S., Sorensen, L.G., Olsen, O.H. & Jacobsen, P. J. Med. Chem. 47, 400–410 (2004).
Ebdrup, S., Refsgaard, H.H., Fledelius, C. & Jacobsen, P. J. Med. Chem. 50, 5449–5456 (2007).
Schweiger, M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 40236–40241 (2006).
Wilson, P.A., Gardner, S.D., Lambie, N.M., Commans, S.A. & Crowther, D.J. J. Lipid Res. 47, 1940–1949 (2006).
Das, S.K. et al. Science 333, 233–238 (2011).
Tisdale, M.J. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 26, 146–151 (2010).
Honors, M.A. & Kinzig, K.P. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 3, 5–11 (2012).
Haemmerle, G. et al. Nat. Med. 17, 1076–1085 (2011).
Hirano, K. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 16, 702–705 (2009).
Taschler, U. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 286, 17467–17477 (2011).
Kienesberger, P.C. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 5908–5917 (2008).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Austrian Science Fund (FWF) projects (W901-B05 DK Molecular Enzymology (R. Zimmermann, R.B.), Translational Program TRP4 (R. Zimmermann), Wittgenstein Award 2007 (grant no. Z136, R. Zechner)) and by the Forschungsförderungsgesellschaft und Bundesministerium für Wissenschaft und Forschung (Austrian Genome Project GEN-AU: Genomics of Lipid-Associated Disorders (GOLD, R. Zechner, R. Zimmermann) and Platform for Chemical Biology in Austria (PLACEBO, R.B.)). We are grateful to B. Grumm and B. Wölfl for skillful help in the synthesis of Atglistatin. Furthermore, we thank P. Jacobsen and H. Tornqvist from Novo Nordisk for helpful discussions and for the provision of lead compounds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R. Zimmermann, R.B., R. Zechner, G.H. and C.F. conceived the study design. N.M., M.S., M.R., T.O.E., J.I., E.F., G.F.G., A.L., C.H. and I.M. performed the experiments. R. Zimmermann and R.B. analyzed the data and wrote the paper. All of the authors read, revised and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
N.M., M.S., M.R., R. Zimmermann and R.B. have filed for a patent on lipase inhibitors.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Results, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Figures 1–9 and Supplementary Note. (PDF 3322 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer, N., Schweiger, M., Romauch, M. et al. Development of small-molecule inhibitors targeting adipose triglyceride lipase. Nat Chem Biol 9, 785–787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1359
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1359
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Fatty acid desaturation by stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 controls regulatory T cell differentiation and autoimmunity
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2023)
-
Dynamic enlargement and mobilization of lipid droplets in pluripotent cells coordinate morphogenesis during mouse peri-implantation development
Nature Communications (2022)
-
A global lipid map reveals host dependency factors conserved across SARS-CoV-2 variants
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Therapeutic strategy targeting host lipolysis limits infection by SARS-CoV-2 and influenza A virus
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2022)
-
Perilipin 5 links mitochondrial uncoupled respiration in brown fat to healthy white fat remodeling and systemic glucose tolerance
Nature Communications (2021)