Abstract
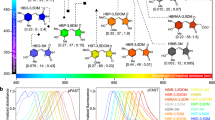
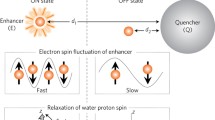
Existing magnetic resonance reporter genes all rely on the presence of (super)paramagnetic substances and employ water relaxation to gain contrast. We designed a nonmetallic, biodegradable, lysine rich–protein (LRP) reporter, the prototype of a potential family of genetically engineered reporters expressing artificial proteins with frequency-selective contrast. This endogenous contrast, based on transfer of radiofrequency labeling from the reporter's amide protons to water protons, can be switched on and off.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Louie, A.Y. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 18, 321–325 (2000).
Weissleder, R. et al. Nat. Med. 6, 351–355 (2000).
Bulte, J.W.M. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 19, 1141–1147 (2001).
Modo, M. et al. Neuroimage 21, 311–317 (2004).
Cohen, B., Dafni, H., Meir, G., Harmelin, A. & Neeman, M. Neoplasia 7, 109–117 (2005).
Genove, G., DeMarco, U., Xu, H., Goins, W.F. & Ahrens, E.T. Nat. Med. 11, 450–454 (2005).
Ward, K.M., Aletras, A.H. & Balaban, R.S. J. Magn. Reson. 143, 79–87 (2000).
Goffeney, N., Bulte, J.W.M., Duyn, J., Bryant, L.H., Jr. & van Zijl, P.C.M. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123, 8628–8629 (2001).
Zhang, S., Merritt, M., Woessner, D.E., Lenkinski, R.E. & Sherry, A.D. Acc. Chem. Res. 36, 783–790 (2003).
Terreno, E., Castelli, D.D., Cravotto, G., Milone, L. & Aime, S. Invest. Radiol. 39, 235–243 (2004).
Zhou, J. & van Zijl, P.C.M. Progr. NMR Spectr. 48, 109–136 (2006).
Zhou, J., Payen, J.F., Wilson, D.A., Traystman, R.J. & van Zijl, P.C.M. Nat. Med. 9, 1085–1090 (2003).
Zhou, J., Lal, B., Wilson, D.A., Laterra, J. & van Zijl, P.C.M. Magn. Reson. Med. 50, 1120–1126 (2003).
Jones, C.K. et al. Magn. Reson. Med. 56, 585–592 (2006).
McMahon, M.T. et al. Magn. Reson. Med. 55, 836–847 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank D.A. Kedziorek, V.P. Chacko and J. Zhang for experimental assistance. Supported by National Institutes of Health grants CA103175, NS045062, EB005252 and K01 EB006394.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
We have applied for a patent for the technology described in the paper.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilad, A., McMahon, M., Walczak, P. et al. Artificial reporter gene providing MRI contrast based on proton exchange. Nat Biotechnol 25, 217–219 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1277
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1277
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Genomically mined acoustic reporter genes for real-time in vivo monitoring of tumors and tumor-homing bacteria
Nature Biotechnology (2023)
-
Computationally designed dual-color MRI reporters for noninvasive imaging of transgene expression
Nature Biotechnology (2022)
-
Genetically encodable materials for non-invasive biological imaging
Nature Materials (2021)
-
A biological multiplexer, designs, and simulations
The Journal of Supercomputing (2021)
-
Redesigned reporter gene for improved proton exchange-based molecular MRI contrast
Scientific Reports (2020)