Abstract
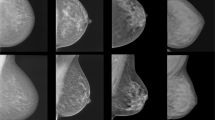
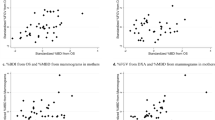
Previous investigators have shown that there is a strong association between the fraction of fibroglandular tissue within the breast as determined by X-ray mammography (per cent density) and breast cancer risk. In this study, the quantitative correlation between per cent density and two objective magnetic resonance (MR) parameters of breast tissue, relative water content and mean T2 relaxation time, as investigated for 42 asymptomatic subjects. Using newly developed, rapid techniques MR measurements were performed on a volume-of-interest incorporating equal, representative portions of both breasts. X-ray mammograms of each subject were digitised and analysed semiautomatically to determine per cent density. Relative water content showed a strong positive correlation with per cent density (Pearson correlation coefficient rp = 0.79, P < 0.0001) and mean T2 value showed a strong negative correlation with per cent density (rp = -0.61, P < 0.0001). The MR and X-ray parameters were also associated with sociodemographic and anthropometric risk factors for breast cancer (P < 0.05). The potential use of MR parameters to assess risk of breast cancer and to provide a frequent, non-hazardous monitor of breast parenchyma is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graham, S., Bronskill, M., Byng, J. et al. Quantitative correlation of breast tissue parameters using magnetic resonance and X-ray mammography. Br J Cancer 73, 162–168 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.30
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1996.30
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The distribution of breast density in women aged 18 years and older
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2024)
-
Alternative methods to measure breast density in younger women
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
Bilateral symmetry of breast tissue composition by magnetic resonance in young women and adults
Cancer Causes & Control (2014)
-
Mammographic density is not a worthwhile examination to distinguish high cancer risk women in screening
European Radiology (2014)
-
Optical imaging correlates with magnetic resonance imaging breast density and revealscomposition changes during neoadjuvant chemotherapy
Breast Cancer Research (2013)