Abstract
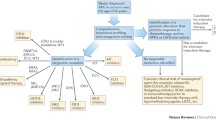
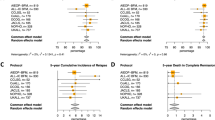
Resistance to cytotoxic agents may be encountered during the treatment of acute myeloblastic leukaemia (AML). P-glycoprotein encoded by the MDR-1 gene has been implicated as a potential drug resistance mechanism in leukaemic cells. In recent years, many data have been accrued concerning the expression of P-glycoprotein in leukaemia, and several studies have been published which have related MDR status to outcome in AML. Conclusions as to the effect of P-glycoprotein expression on prognosis in AML have varied widely. The studies are not immediately comparable, since they differ in methodology, treatment regimens, demographic profile and, perhaps most importantly, criteria for positivity of MDR status. The technique of statistical overview (meta-analysis) can be used to pool observational studies. Application of this statistical method to existing studies suggests an estimated relative risk of 0.68 for P-glycoprotein expression with respect to complete remission in AML. Further large studies are required to determine fully the role of P-glycoprotein in AML.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holmes, J., West, R. The effect of MDR-1 gene expression on outcome in acute myeloblastic leukaemia. Br J Cancer 69, 382–384 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.70
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.70
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Association between P-glycoprotein and lymphoid antigen expression on myeloblasts versus therapy response and survival in de novo acute myeloid leukemia: long-term follow-up results
Medical Oncology (2012)
-
Combined action of PSC 833 (Valspodar), a novel MDR reversing agent, with mitoxantrone, etoposide and cytarabine in poor-prognosis acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2001)