Abstract
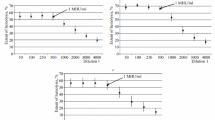
Serum complement levels were assayed in 26 patients with disseminated cancer, who received immunotherapy with infusion of C. parvum. Complement activation, indicated by the consumption of C3 or C4 or both, was found in 46% of the patients. Serum samples showed direct correlation between decreased C3 and conversion of C3 proactivator, whereas such conversion did not occur when C4 alone was decreased. It is concluded that the bypass (properdin) pathway was activated in patients in whom C3 consumption was detected, while the classical (C1) pathway was activated in the patients with C4 consumption unaccompanied by C3 decrease. Direct correlation was observed between delayed cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions to recall antigens and the incidence of C. parvum-associated complement activation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biran, H., Moake, J., Reed, R. et al. Complement activation in vivo in cancer patients receiving C. parvum immunotherapy. Br J Cancer 34, 493–499 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1976.203
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1976.203
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Personal experience withCorynebacterium parvum in human cancers
World Journal of Surgery (1977)