Abstract
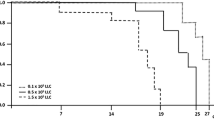
Intrapleurally injected cells of an ascitic rat tumour produced intrapleural effusions and solid pleural deposits. BCG, or its methanol extraction residue (MER) injected into the pleural space, suppressed tumour development and prolonged survival. Treatment was effective if given a few days before or after tumour injection. In contrast, active specific immunotherapy by repeated s.c. injection of viable or radiation-attenuated tumour cells in admixture with BCG was unsuccessful, and did not improve the response to intrapleural BCG treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pimm, M., Hopper, D. & Baldwin, R. BCG treatment of malignant pleural effusions in the rat. Br J Cancer 34, 368–373 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1976.179
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1976.179
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Histopathology of BCG and thiotepa treated bladders
Urological Research (1986)
-
Antitumor monoclonal antibodies for radioimmunodetection of tumors and drug targeting
CANCER AND METASTASIS REVIEW (1983)