Abstract
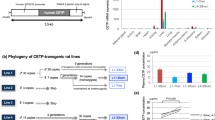
Spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR) display several features of the human insulin-resistance syndromes. Cd36 deficiency is genetically linked to insulin resistance in SHR. We show that transgenic expression of Cd36 in SHR ameliorates insulin resistance and lowers serum fatty acids. Our results provide direct evidence that Cd36 deficiency can promote defective insulin action and disordered fatty-acid metabolism in spontaneous hypertension.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aitman, T.J. et al. Nature Genet. 16, 197–201 (1997).
Abumrad, N.A., Elmaghrabi, M.R., Amri, E.Z., Lopez, E. & Grimaldi, P.A. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 17665–17668 (1993).
Aitman, T.J. et al. Nature Genet. 21, 76–83 (1999).
Pravenec, M. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 1651–1657 (1999).
Febbraio, M. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 19055–19062 (1999).
Gotoda, T. et al. Nature Genet. 22, 226–228 (1999).
Boden, G. Diabetes 46, 3–10 (1997).
Shulman, G.I. J. Clin. Invest. 106, 171–176 (2000).
Ibrahimi, A. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 2646–2651 (1996).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants 301/00/1636 and 204/98/K015 from the Grant Agency of the Czech Republic to V.Z. and M.P.; grant LN00A079 from the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic to M.P.; NIH grants RO1 HL56028 and PO1 HL35018 (project 2) to T.W.K. and RO1 HL63709 to E.M.St.L.; and grant 4904-3 from the Internal Grant Agency of the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic to L.K. T.J.A. was supported by intramural funding from the MRC Clinical Sciences Center and A.M.G. was supported by an MRC Studentship (G78/5347). M.P. is an International Research Scholar of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute and E.M.St.L. is a recipient of a Mentored Clinical Scientist Award from the NIH/NHLBI.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pravenec, M., Landa, V., Zidek, V. et al. Transgenic rescue of defective Cd36 ameliorates insulin resistance in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Nat Genet 27, 156–158 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/84777
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84777
- Springer Nature America, Inc.
This article is cited by
-
Rat models of human diseases and related phenotypes: a systematic inventory of the causative genes
Journal of Biomedical Science (2020)
-
A scan for genes associated with cancer mortality and longevity in pedigree dog breeds
Mammalian Genome (2020)
-
Sex-specific differences in hepatic steatosis in obese spontaneously hypertensive (SHROB) rats
Biology of Sex Differences (2018)
-
Changes in the activity of some metabolic enzymes in the heart of SHR rat incurred by transgenic expression of CD36
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry (2018)
-
Translational regulation shapes the molecular landscape of complex disease phenotypes
Nature Communications (2015)