Abstract
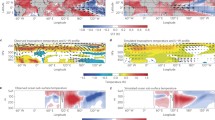
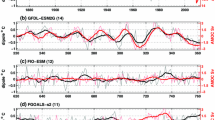
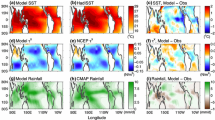
Rainfall variability in northeast South America1 and the Sahel region of Africa2–4 is profoundly influenced by the sea surface temperature (SST) of the tropical Atlantic Ocean. Of particular importance are relative changes in SST between the hemispheres on decadal timescales, a phenomenon often called the Atlantic SST dipole1,5. Here we propose that the decadal variation in the tropical SST dipole may be attributed to an unstable thermodynamic ocean–atmosphere interaction between wind-induced heat fluxes and SST. Using coupled ocean–atmosphere models, we show that the coupled dipole mode has a typical oscillation period of about a decade. The notion that the Atlantic dipole-like SST variability may be related to an oscillatory coupled mode might assist attempts to predict decadal climate variability in the tropical Atlantic region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moura, A. D. & Shukla, J. J. Atmos. Sci. 38, 2653–2675 (1981).
Lamb, P. J. Tellus A 35, 198–212 (1983).
Hastenrath, S. Mon. Weath. Rev. 112, 1097–1107 (1984).
Folland, C., Palmer, T. & Parker, D. Nature 320, 602–607 (1986).
Servain, J. J. Geophys. Res. 96, 15137–15146 (1991).
Philander, S. G. El Niño, La Niña, and the Southern Oscillation (Academic, New York, 1990).
Zebiak, S. J. Clim. 6, 1567–1586 (1993).
Mehta, V. M. & Delworth, T. J. Clim. 5, 172–190 (1995).
Mann, M. E. & Park, J. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 25819–25833 (1994).
da Silva, A., Young, A. C. & Levitus, S. Atlas of Surface Marine Data 1994, Vol. 1, Algorithms and Procedures (NOAA Atlas NESDIS 6) (US Dept Commerce, Washington DC, 1994).
Bretherton, C. S., Smith, C. & Wallace, J. M. J. Clim. 5, 541–560 (1992).
Carton, J. A., Cao, X., Giese, B. S. & da Silva, A. J. Phys. Oceanogr. (in the press).
Zhou, Z. thesis, Univ. Maryland (1996).
Frankignoul, C. & Hasselmann, K. Tellus 29, 284–305 (1977).
Zebiak, S. E. & Cane, M. A. Mon. Weath. Rev. 115, 2262–2278 (1987).
Chang, P. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 7725–7741 (1994).
Chang, P., Ji, L. & Flügel, M. Physica D (in the press).
Syu, H. H., Neelin, J. D. & Gutzler, D. J. Clim. 8, 2121–2143 (1995).
Neelin, D. J. Atmos. Sci. 48, 584–606 (1991).
Parker, D. E., Jones, P. D., Folland, C. K. & Bevan, A. J. Geophys. Res. 99, 14373–14399 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, P., Ji, L. & Li, H. A decadal climate variation in the tropical Atlantic Ocean from thermodynamic air-sea interactions. Nature 385, 516–518 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385516a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385516a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Increase in ocean-onto-land droughts and their drivers under anthropogenic climate change
npj Climate and Atmospheric Science (2023)
-
Pan-Atlantic decadal climate oscillation linked to ocean circulation
Communications Earth & Environment (2023)
-
Cross-seasonal influence of the North Tropical Atlantic SST on soil moisture in Northeastern Eurasia
Climate Dynamics (2023)
-
Weakened interannual Tropical Atlantic variability in CMIP6 historical simulations
Climate Dynamics (2023)
-
Understanding the interplay between ENSO and related tropical SST variability using linear inverse models
Climate Dynamics (2023)