Abstract
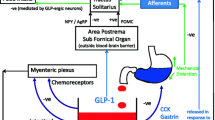
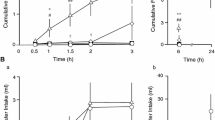
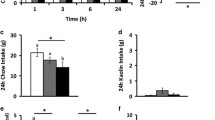
THE sequence of glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–36) amide (GLP-1) is completely conserved in all mammalian species studied, implying that it plays a critical physiological role1. We have shown that GLP-1 and its specific receptors are present in the hypo-thalamus2,3. No physiological role for central GLP-1 has been established. We report here that intracerebroventricular (ICV) GLP-1 powerfully inhibits feeding in fasted rats. ICV injection of the specific GLP-1-receptor antagonist, exendin (9-39)4, blocked the inhibitory effect of GLP-1 on food intake. Exendin (9-39) alone had no influence on fast-induced feeding but more than doubled food intake in satiated rats, and augmented the feeding response to the appetite stimulant, neuropeptide Y. Induction of c-fos is a marker of neuronal activation5. Following ICV GLP-1 injection, c-fos appeared exclusively in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and central nucleus of the amygdala, and this was inhibited by prior administration of exendin (9-39). Both of these regions of the brain are of primary importance in the regulation of feeding6. These findings suggest that central GLP-1 is a new physiological mediator of satiety.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orskov, C. Diabetologia 35, 701–711 (1992).
Kreymann, B. et al. Brain Res. 502, 325–331 (1989).
Kanse, S. M., Kreymann, B., Ghatei, M. A. & Bloom, S. R. FEBS Lett. 241, 209–212 (1988).
Goke, R. et al. J. biol. Chem. 268, 19650–19655 (1993).
Sagar, S. M., Sharp, F. R. & Curran, T. Science 240, 1328–1331 (1988).
Morley, J. E. Endocr. Rev. 8, 256–287 (1987).
Antin, J., Gibbs, J., Holt, J., Young, R. C. & Smith, G. P. J. comp. Physiol. Psychol. 89, 784–790 (1975).
Chow, H. L. & Beck, C. H. Eur. J. Pharmac. 102, 297–304 (1984).
Wilding, J. P. et al. J. Endocr. 132, 299–304 (1992).
Blundell, J. E., Rogers, P. J. & Hill, A. J. Brain Res. Bull. 15, 371–376 (1985).
Suzuki, S., Kawai, K., Ohashi, S., Mukai, H. & Yamashita, K. Endocrinology 125, 3109–3114 (1989).
Rai, A., Singh, G., Raffaniello, R., Eng, J. & Raufman, J. P. Am. J. Physiol 265, G118–125 (1993).
Wang, Z. et al. J. clin. Invest. 95, 417–421 (1995).
Kulkarni, R. N. et al. Reg. Pept. 57, 201 (1995).
Billington, C. J., Levine, A. S. & Morley, J. E. Am. J. Physiol. 245, R920–926 (1983).
Clark, J. T., Kalra, P. S. & Kalra, S. P. Endocrinology 117, 2435–2442 (1985).
Lambert, P. D. et al. Endocrinology 133, 29–32 (1993).
Wilding, J. P., Gilbey, S. G., Lambert, P. D., Ghatei, M. A. & Bloom, S. R. Neuroendocrinology. 57, 581–587 (1993).
Pelleymounter, M. A. et al. Science 269, 540–543 (1995).
Halaas, J. L. et al. Science 269, 543–546 (1995).
Campfield, L. A., Smith, F. J., Guisez, Y., Devos, R. & Burn, P. Science 269, 546–549 (1995).
Veale, P. R., Bhogal, R., Morgan, D. G., Smith, D. M. & Bloom, S. R. Eur. J. Pharmac. 262, 133–141 (1994).
Lambert, P. D., Phillips, P. J., Wilding, J. P. H., Bloom, S. R. & Herbert, J. Brain Res. 670, 59–65 (1995).
Arnold, F. J. et al. Neuroscience 51, 377–390 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turton, M., O'Shea, D., Gunn, I. et al. A role for glucagon-like peptide-1 in the central regulation of feeding. Nature 379, 69–72 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379069a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379069a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
A GIPR antagonist conjugated to GLP-1 analogues promotes weight loss with improved metabolic parameters in preclinical and phase 1 settings
Nature Metabolism (2024)
-
Obesogens: a unifying theory for the global rise in obesity
International Journal of Obesity (2024)
-
Pharmacokinetics and brain distribution of the therapeutic peptide liraglutide by a novel LC–MS/MS analysis
Journal of Analytical Science and Technology (2023)
-
Efficacy and safety of tirzepatide, dual GLP-1/GIP receptor agonists, in the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome (2023)
-
The future of incretins in the treatment of obesity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Diabetologia (2023)