Abstract
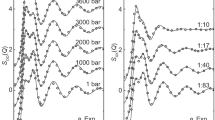
THE characteristic tetrahedral structure of water is known to be disrupted by changes in pressure and temperature1–3. It has been suggested that ions in solution may have a similar perturbing effect4,5. Here we use neutron diffraction to compare the effects of applied pressure and high salt concentrations on the hydrogen-bonded network of water. We find that the ions induce a change in structure equivalent to the application of high pressures, and that the size of the effect is ion-specific. Ionic concentrations of a few moles per litre have equivalent pressures that can exceed a thousand atmospheres. We propose that these changes may be understood in terms of the partial molar volume of the ions, relative to those of water molecules. The equivalent induced pressure of a particular ion species is correlated with its efficacy in precipitating, or salting-out, proteins from solution6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Postorino, P., Tromp, R. H., Ricci, M.-A., Soper, A. K. & Nielson, G. W. Nature 366, 668–670 (1993).
Postorino, P., Ricci, M. A. & Soper, A. K. J. chem. Phys. 101, 4123–4132 (1994).
Tromp, R. H., Posterino, P., Neilson, G. W., Ricci, M. A. & Soper, A. K. J. chem. Phys. 101, 6210–6215 (1994).
Tromp, R. H., Neilson, G. W. & Soper, A. K. J. chem. Phys. 96, 8460–8469 (1992).
Enderby, J. E., Howells, W. S. & Howe, R. A. Chem. Phys. Lett. 21, 109–112 (1973).
Hofmeister, F. Arch. Exp. Path. Pharmakol. 24, 247–260 (1888).
Zubay, G. Biochemistry 3rd Edn (Brown, Dubuque, IA, 1993).
Herdman, G. J. & Neilson, G. W. J. Molec. Liq. 46, 165–179 (1990).
Soper, A. K., Howells, W. S. & Hannon, A. C. ATLAS: Analysis of Time-of-flight Diffraction Data from Liquid and Amorphous Samples (Rep. No. 89-046, Rutherford Appleton Lab., Chilton, 1989).
Soper, A. K. & Luzar, A. J. chem. Phys. 97, 1320–1331 (1993).
Soper, A. K. & Tumer, J. Z. Int. J. mod. Phys. 7, 3049–3076 (1993).
Soper, A. K. & Phillips, M. C. Chem. Phys. 107, 47–60 (1993).
Millero, F. J. Chem. Rev. 72, 147–176 (1971).
Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 55th Edn D194–D236 (CRC, Cleveland, 1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leberman, R., Soper, A. Effect of high salt concentrations on water structure. Nature 378, 364–366 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/378364a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/378364a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Leidenfrost green synthesis method for MoO3 and WO3 nanorods preparation: characterization and methylene blue adsorption ability
BMC Chemistry (2023)
-
Effect of alkali metal ions on water structure: insights into the pressure-like effect
Structural Chemistry (2023)
-
Cryo-SEM and confocal LSM studies of agar gel, nanoparticle hydrocolloid, mineral clays and saline solutions
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Dissolving salt is not equivalent to applying a pressure on water
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Thermal conductivity of hybrid multilayer graphene-fiber carbon membranes
Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry (2022)