Abstract
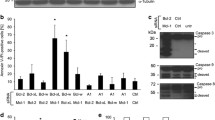
CELLS are eliminated in a variety of physiological settings by apoptosis, a genetically encoded process of cellular suicide1,2. Apoptosis comprises an intrinsic cellular defence against tumorigenesis, which, when suppressed, may contribute to the development of malignancies3. The bcl-2oncogene, which is activated in follicular lymphomas, functions as a potent suppressor of apoptosis under diverse conditions4. Here we describe the complementary DNA cloning and functional analysis of a new Bcl-2 homologue, Bak, which promotes cell death and counteracts the protection from apoptosis provided by Bcl-2. Moreover, enforced expression of Bak induces rapid and extensive apoptosis of serum-deprived fibroblasts. This raises the possibility that Bak is directly involved in activating the cell death machinery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr, J., Wyllie, A. & Currie, A. Br. J. Cancer 26, 239–257 (1972).
Ellis, R. E., Yuan, J. Y. & Horvitz, H. R. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 7, 663–698 (1991).
Fisher, D. Cell 78, 539–542 (1994).
Reed, J. J. Cell Biol. 124, 1–6 (1994).
Yin, X. M., Oltval, Z. N. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Nature 369, 321–323 (1994).
Boise, L. H. et al. Cell 74, 597–608 (1993).
Hockenbery, D., Nunez, G., Milliman, C., Schreiber, R. D. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Nature 348, 334–336 (1990).
Kolodziej, P. & Young, R. Meth. Enzym. 194, 508–519 (1991).
Oltvai, Z., Milliman, C. & Korsmeyer, S. Cell 74, 609–619 (1993).
Evan, G. et al. Cell 63, 119–125 (1992).
Fanidi, A., Harrington, E. & Evan, G. Nature 359, 554–556 (1992).
Harrington, E., Fanidi, A., Bennett, M. & Evan, G. EMBO J. 13, 3286–3295 (1994).
Braselmann, S., Graninger, P. & Busslinger, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 1657–1661 (1993).
Rao, L. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci U.S.A. 89, 7742–7746 (1992).
Smeyne, R. et al. Nature 363, 166–169 (1993).
Wu, X. & Levine, A. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91, 3602–3606 (1994).
Farrow, S. N. et al. Nature 374, 731–733 (1995).
Kiefer, M. C. et al. Nature 374, 736–739 (1995).
Lin, E., Orlofsky, A., Berger, M. & Prystowsky, M. J. Immun. 151, 1979–1988 (1993).
Kozopas, K. M., Yang, T., Buchan, H. L., Zhou, P. & Craig, R. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 3516–3520 (1993).
Williams, G. & Smith, C. Cell 74, 777–779 (1993).
Morgenstern, J. P. & Land, H. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 3587–3596 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chittenden, T., Harrington, E., O'Connor, R. et al. Induction of apoptosis by the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature 374, 733–736 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/374733a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/374733a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Modulating Nrf-2/HO-1, apoptosis and oxidative stress signaling pathways by gabapentin ameliorates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology (2024)
-
MicroRNA profiling of royal jelly extracellular vesicles and their potential role in cell viability and reversing cell apoptosis
Functional & Integrative Genomics (2023)
-
Protective role of ABCA1 in ischemic preconditioning is mediated by downregulation of miR-33-5p and miR-135-5p
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
BCL2L13: physiological and pathological meanings
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Protective effect of Moringa oleifera leaves ethanolic extract against thioacetamide-induced hepatotoxicity in rats via modulation of cellular antioxidant, apoptotic and inflammatory markers
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2019)