Abstract
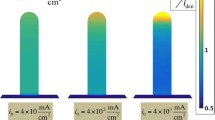
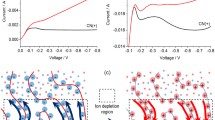
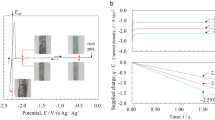
ELECTRODEPOSITION of metals such as copper and zinc from solutions of their salts may give rise to ramified metal deposits which show a range of growth morphologies1–9. Our understanding of the factors that determine growth morphology is still very limited, in part because different morphologies may be observed even under similar growth conditions4,5. It is thought9 that uncontrolled convective processes at the tips of the deposit branches may play a role in these discrepancies. Here we show that convective effects, which we can visualize directly, in the electrodeposition of iron from FeSO4 solution, can generate a mesh-like pattern, a morphology that has not been reported previously. Convection can be diminished by altering the pH, whereupon we see a transition to a dense branching morphology. Our results show that convective effects do indeed play an important part in determining pattern selection during electrodeposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kessler, D. A., Koplik, J. & Levine, H. Adv. Pbys. 37, 255–339 (1988).
Brady, R. M. & Ball, R. C. Nature 309, 225–229 (1984).
Matsushita, M., Sano, M., Hayakawa, Y., Honjo, H. & Sawada, Y. Phys. Rev. Lett. 53, 286–289 (1984).
Sawada, Y., Dougherty, A. & Gollub, J. P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 1260–1263 (1986).
Grier, D., Ben-Jacob, E., Clarke, R. & Sander, L. M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 56, 1264–1267 (1986).
Argoul, F., Arneodo, A., Grasseau, G. & Swinney, H. L. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61, 2558–2561 (1988).
Garik, P. et al. Phys. Rev. Lett. 62, 2703–2706 (1989).
Melrose, J. R., Hibbert, D. B. & Ball, R. C. Phys. Rev. Lett. 65, 3009–3012 (1990).
Fleury, V., Chazalviel, J.-N. & Rosso, M. Phys. Rev. Lett. 68, 2492–2495 (1992); Phys. Rev. E48, 1279–1295 (1993).
Fukunaka, Y., Yamamoto, T. & Kondo, Y. J. electrochem. Soc. 136, 3630–3633 (1989).
Wang, M. & Ming, N.-B. Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 113–116 (1993).
Garik, P., Hetrick, J., Orr, B., Barkey, D. & Ben-Jacob, E. Phys. Rev. Lett. 66, 1606–1609 (1991).
Wang, M. & Ming, N.-B. Phys. Rev. A45, 2493–2498 (1992).
Cotton, F. A. & Wilkinson, F. R. S. G. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry 2nd edn (Wiley, New York 1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., van Enckevort, W., Ming, Nb. et al. Formation of a mesh-like electrodeposit induced by electroconvection. Nature 367, 438–441 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367438a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367438a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Linking origin of the electric field-assisted β-PbF2 crystallization in lead oxyfluoroborate glasses below T g to simultaneous cathode/anode-compensated electrochemical reactions
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2012)