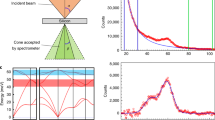
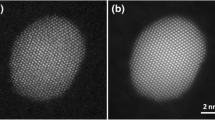
Abstract
THE high angle elastic scattering of electrons in scanning transmission electron microscopy depends strongly on the atomic number Z, of the sample atoms, through the Z2 dependence of the Rutherford scattering cross-section1. The detection of scattered electrons at high angles and over a large angular range (75& ndash;150 milliradians) removes the coherent effects of diffraction, and the resulting incoherent image provides a compositional map of the sample with high atomic-number contrast1. If a fine electron probe is used, and the sample is a crystalline material oriented along one of its principal axes, individual columns of atoms can be imaged in this way2. Electrons scattered at low angles are not used in this detection scheme, and are thus available for simultaneous electron energy-loss spectroscopy3; in principle, this combination of techniques should allow the direct chemical analysis of single atomic columns in crystalline materials. Here we present electron energy-loss spectra from expitaxial interfaces between cobalt silicide and silicon, which confirm that atomic resolution can be achieved by this approach. The ability to correlate structure and chemistry with atomic resolution holds great promise for the detailed study of defects and interfaces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pennycook, S. J. & Boatner, L. A. Nature 336, 565–567 (1988).
Pennycook, S. J. & Jesson, D. E. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 938–941 (1990); Acta Metall. Mater. 40, S149–S159 (1992).
Crewe, A. V., Wall, J. & Langmore, J. Science 168, 1338–1340 (1970).
Jesson, D. E. & Pennycook, S. J. in 51st A. Proc. Microsc. Soc. Am. (eds Bailey, G. W. & Rieder, C. L.) 978–979 (San Francisco Press, California, 1993).
Loane, R. F., Xu, P. & Silcox, J. Ultramicroscopy 40, 121–138 (1992).
Browning, N. D. & Pennycook, S. J. Microbeam Analysis 2, 81–89 (1993).
Browning, N. D., McGibbon, M. M., Chisholm, M. F. & Pennycook, S. J. in 51st A. Proc. Microsc. Soc. Am. (eds Bailey, G. W. & Rieder, C. L.) 576–577 (San Francisco Press, California, 1993).
Pennycook, S. J. Contemp. Phys. 23, 371–400 (1982).
Kohl, H. & Rose, H. Adv. Electron. Electron Phys. 65, 175–200 (1985).
Ritchie, R. H. & Howie, A. Phil. Mag. A58, 753–767 (1988).
Allen, L. J. & Rossouw, C. J. Phys. Rev. B42, 11644–11654 (1990).
Scheinfein, M. R. & Isaacson, M. S. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B4, 326–332 (1986).
Batson, P. E. Phys. Rev. B44, 5556–5561 (1991).
Browning, N. D., Yuan, J. & Brown, L. M. Phil. Mag. A67, 261–271 (1993).
Browning, N. D., Chisholm, M. F., Pennycook, S. J., Norton, D. P. & Lowndes, D. H. Physica C212, 185–190 (1993).
Batson, P. E. Ultramicroscopy 47, 133–144 (1992).
de Jong, A. F. & Bulle-Liewma, C. W. T. Phil. Mag. A62, 183–201 (1990).
Chisholm, M. F., Jesson, D. E., Pennycook, S. J. & Mantl, S. in 51st A. Proc. Microsc. Soc. Am. (eds Bailey, G. W. & Rieder, C. L.) 802–803 (San Francisco Press, California, 1993).
De Crescenzi, M., Derrien, J., Chainet, E. & Orumchian, K. Phys. Rev. B39, 5520–5523 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Browning, N., Chisholm, M. & Pennycook, S. Atomic-resolution chemical analysis using a scanning transmission electron microscope. Nature 366, 143–146 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/366143a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/366143a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Causal analysis of competing atomistic mechanisms in ferroelectric materials from high-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy data
npj Computational Materials (2020)
-
Graphene-supported metal single-atom catalysts: a concise review
Science China Materials (2020)
-
Three-dimensional localization of nanoscale battery reactions using soft X-ray tomography
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Misfit Strain Relaxation of Ferroelectric PbTiO3/LaAlO3 (111) Thin Film System
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Atomic-scale Chemical Imaging and Quantification of Metallic Alloy Structures by Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy
Scientific Reports (2014)