Abstract
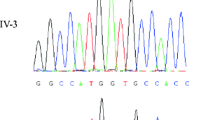
FAMILIAL male precocious puberty (FMPP) is a gonadotropin-independent disorder that is inherited in an autosomal dominant, male-limited pattern1–5. Affected males generally exhibit signs of puberty by age 4. Testosterone production and Ley dig cell hyper-plasia occur in the context of prepubertal levels of luteinizing hormone (LH)3–5. The LH receptor is a member of the family of G-protein-coupled receptors6,7, and we hypothesized that FMPP might be due to a mutant receptor that is activated in the presence of little or no agonist8–12. A single A → G base change that results in substitution of glycine for aspartate at position 578 in the sixth transmembrane helix of the LH receptor was found in affected individuals from eight different families. Linkage of the mutation to FMPP was supported by restriction-digest analysis. COS-7 cells expressing the mutant LH receptor exhibited markedly increased cyclic AMP production in the absence of agonist, suggesting that autonomous Leydig cell activity in FMPP is caused by a constitutively activated LH receptor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stone, R. K. Am. J. med. Sci. 24, 561–564 (1852).
Walker, S. H. J. Pediat. 41, 251–257 (1952).
Schedewie, H. K. et al. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 57, 271–278 (1981).
Rosenthal, S. M., Grumbach, M. M. & Kaplan, S. L. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 57, 571–578 (1983).
Holland, F. J. Endocr. Metab. Clin. North Am. 20, 191–210 (1991).
Minegishi, T. et al. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 172, 1049–1054 (1990).
Jia, X-C. et al. Molec. Endocr. 5, 759–768 (1991).
Allen, L. F., Lefkowitz, R. J., Caron, M. G. & Cotecchia, S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 11354–11358 (1991).
Kjelsberg, M. A., Cotecchia, S., Ostrowski, J., Caron, M. G. & Lefkowitz, R. J. J. biol. Chem. 267, 1430–1433 (1992).
Samama, P., Cotecchia, S., Costa, T. & Lefkowitz, R. J. J. biol. Chem 268, 4625–4636 (1993).
Ren, Q., Kurose, H., Lefkowitz, R. J. & Cotecchia, S. J. biol. Chem 268, 16483–16487 (1993).
Kosugi, S., Okajima, F., Ban, T., Hidaka, A., Shenker, A. & Kohn, L. D. Molec Endocr. 7, 1009–1020 (1993).
Riesner, D. et al. Electrophoresis 10, 377–389 (1989).
Hunzicker-Dunn, M. & Birnbaumer, L. in Luteinizing Hormone Action and Receptors (ed Ascoli, M.) 57–134 (CRC, Boca Raton, 1985).
Oerter, K. E., Uriarte, M., Rose, S. R., Barnes, K. M. & Cutler, G. B. Jr J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 71, 1251–1258 (1990).
Sklar, C. A., Conte, F. A., Kaplan, S. L. & Grumbach, M. M. J. clin. Endocr. Metab. 53, 656–660 (1981).
Baldwin, J. M. EMBO J. 12, 1693–1703 (1993).
Trumpp-Kallmeyer, S., Hoflack, J., Bruinvels, A. & Hibert, M. J. Med. Chem. 35, 3448–3462 (1992).
Neitz, M., Neitz, J. & Jacobs, G. J. Science 252, 971–974 (1991).
Tsai-Morris, C. H., Buczko, E., Wang, W. & Dufau, M. L. J. biol. Chem. 265, 19385–19388 (1990).
Bargmann, C. I., Hung, M-C. & Weinberg, R. A. Cell 45, 649–657 (1986).
Yaghmai, R. & Hazelbauer, G. L. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 7890–7894 (1992).
Dryja, T. P. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 323, 1302–1307 (1990).
Rosenthal, W. et al. Nature 359, 233–235 (1992).
Robbins, L. S. et al. Cell 72, 827–834 (1993).
Robinson, P. R., Cohen, G. B., Zhukovsky, E. A. & Oprian, D. D. Neuron 9, 719–725 (1992).
Dryja, T. P., Berson, E. L., Rao, V. R. & Oprian, D. D. Nature Genet. 4, 280–283 (1993).
Myers, R. M., Sheffield, V. C. & Cox, D. R. in PCR Technology: Principles and Applications for DNA Amplification (ed. Erlich, H. A.) 71–88 (Stockton, New York, 1989).
Laue, L., Jones, J., Barnes, K. M. & Cutler, G. B. Jr J. clin. Endocr. Metab 76, 151–155 (1993).
Laue, L. O. H. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 320, 496–502 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shenker, A., Laue, L., Kosugi, S. et al. A constitutively activating mutation of the luteinizing hormone receptor in familial male precocious puberty. Nature 365, 652–654 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/365652a0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/365652a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Adhesion GPR123 is an indicator for recurrence and prognosis in bladder cancer
Genes & Genomics (2021)
-
GPR101 drives growth hormone hypersecretion and gigantism in mice via constitutive activation of Gs and Gq/11
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Novel mutations in LHCGR (luteinizing hormone/choriogonadotropin receptor): expanding the spectrum of mutations responsible for human empty follicle syndrome
Journal of Assisted Reproduction and Genetics (2020)
-
The role of GPCRs in bone diseases and dysfunctions
Bone Research (2019)
-
Central precocious puberty in a case of late-diagnosed familial testotoxicosis and long-term treatment monitoring
Hormones (2018)