Abstract
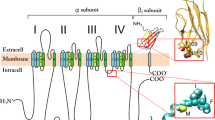
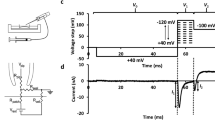
PURIFICATION of skeletal muscle dihydropyridine binding sites has enabled protein complexes to be isolated from which Ca2+ currents have been reconstituted. Complementary DNAs encoding the five subunits of the dihydropyridine receptor, α1, β, γ, α2 and δ (ref. 1), have been cloned2–6 and it is now recognized that α2 and δ are derived from a common precursor7,8. The α1, subunit can itself produce Ca2+ currents, as was demonstrated using mouse L cells lacking α2δ (refs 9,10), β (ref. 10) and γ (our unpublished results). In L cells, stable expression of skeletal muscle α1 alone was sufficient to generate voltage-sensitive, high-threshold L-type Ca2+ channel currents which were dihydropyridine-sensitive and blocked by Cd2+, but the activation kinetics were about 100 times slower than expected for skeletal muscle Ca2+ channel currents. This could have been due to the cell type in which α1 , was being expressed or to the lack of a regulatory component particularly one of the subunits that copurifies with α1. We show here that coexpression of skeletal muscle β with skeletal muscle α1, generates cell lines expressing Ca2+ channel currents with normal activation kinetics as evidence for the participation of the dihydropyridine-receptor β subunits in the generation of skeletal muscle Ca2+ channel currents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Catterall, W. A. Science 242, 50–61 (1988).
Tanabe, T. et al. Nature 328, 313–318 (1987).
Ellis, S. B. et al. Science 241, 1661–1664 (1988).
Ruth, P. et al. Science 245, 1115–1118 (1989).
Jay, S. D. et al. Science 248, 490–492 (1990).
Bosse, E. et al. FEBS Lett. 267, 153–156 (1990).
DeJongh, K. S., Warner, C. & Catterall, W. A. J. blol. Chem. 265, 14738–14741 (1990).
Jay, S. D. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 3287–3293 (1991).
Perez-Reyes, E. et al. Nature 340, 233–236 (1989).
Kim, H. S. et al. J. biol. Chem. 265, 11858–11863 (1990).
Nukada, T., Mishina, M. & Numa, S. FEBS Lett. 211, 5–9 (1987).
Wong, G. G. et al. Science 228, 810–815 (1985).
Liao, C.-F. et al. J. biol. Chem. 264, 7328–7337 (1989).
Hamill, O. P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Pfluegers Arch. ges. Physiol. 391, 85–100 (1981).
Lacerda, A. E. & Brown, A. M. J. gen. Physiol. 93, 1243–1273 (1989).
Cognard, C., Traore, F., Potreau, D. & Raymond, G. Pfluegers Arch. ges. Physiol. 407, 677–638 (1986).
Cognard, C., Romey, G., Galizzi, J.-P., Fosset, M. & Lazdunski, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 1518–1522 (1986).
Brown, A. M., Tsuda, Y. & Wilson, D. L. J. Physiol. 344, 549–583 (1983).
Schwartz, L. M., McCleskey, E. W. & Aimers, W. Nature 314, 747–750 (1985).
Perez-Reyes, E., Wei, X., Castellano, A. & Birnbaumer, L. J. biol. Chem. 265, 20430–20436 (1990).
Mikami, A. et al. Nature 340, 230–233 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lacerda, A., Kim, H., Ruth, P. et al. Normalization of current kinetics by interaction between the α1and β subunits of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Nature 352, 527–530 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/352527a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/352527a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Microdomain–specific localization of functional ion channels in cardiomyocytes: an emerging concept of local regulation and remodelling
Biophysical Reviews (2015)
-
Ion channels and ion transporters of the transverse tubular system of skeletal muscle
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2006)