Abstract
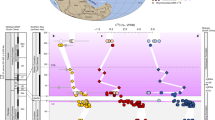
A CRITICAL aspect of the debate over the origin of the chemical, biological and climatological perturbations that characterize the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary (K/T boundary) is the timescale and detailed pattern of the extinctions and geochemical changes. Whether the development of the anomalies was catastrophic (over tens to hundreds of years) or more gradual (103 to 106 years), whether the anomalies occur exactly at the boundary or precede it, and whether the chemical and biological signatures represent one event or can be resolved into several discrete events, are issues fundamental to identifying the cause of the marked changes. To determine the timing and rate of change of strontium isotope evolution of sea water during the five million years preceding the K/T boundary, we analysed foraminifera from an exceptionally thick, palaeontologically well-characterized marine K/T section exposed at Bidart, southwest France. We found a rapid increase in 87Sr/86Sr of ocean water 1.5 to 2.3 Myr before the boundary. The increase may be explained by a 10% increase in continental strontium flux to the oceans over a period of about 1 Myr.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess, J., Bender, M. L. & Schilling, J.-G. Science 231, 979–984 (1986).
Palmer, M. R. & Elderfield, H. Nature 314, 526–528 (1985).
DePaolo, D. J. & Ingram, B. L. Science 227, 938–941 (1985).
Koepnick, R. B. et al. Chem. Geol. 50, 55–81 (1985).
Macdougall, J. D. Science 239, 485–487 (1988).
Javoy, M. & Courtillot, V. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 94, 409–416 (1989).
Perch-Nielsen, K., McKenzie, J. & He, Q. Geol. Soc. Am. Spec. Pap. 190, 353–371 (1982).
Clauser, S. C.R. hebd. Séanc. Sci. Paris 304, 579–584 (1987).
Kent, D. & Gradstein, F. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 96, 1419–1427 (1985).
DePaolo, D. J., Kyte, F. T., Marshall, B. D., O'Neil, J. R. & Smit, J. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 64, 356–373 (1983).
MacLeod, K. G. & Ward, P. D. Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. Progm 22, 266 (1990).
Johnson, C. C. & Kauffman, E. G. in Extinction Events in Earth History (eds Kauffman, E. G. & Walliser, O. H.) 305–307 (Springer, Berlin, 1990).
Officer, C. B. & Drake, C. L. Science 227, 1161–1167 (1985).
Richter, F. M. & DePaolo, D. J. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 83, 27–38 (1987).
Richter, F. M. & DePaolo, D. J. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 90, 382–394 (1988).
DePaolo, D. J. & Finger, K. L. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 103, 112–124 (1991).
Brass, G. W. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 40, 721–730 (1976).
DePaolo, D. J. Geology 14, 103–106 (1986).
Broecker, W. S. & Peng, T.-H. Tracers in the Sea, 1–690 (Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory, Palisades, 1982).
Palmer, M. R. & Edmond, J. M. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 92, 11–26 (1989).
Hodell, D. A., Mueller, P. A. & Garrido, J. R. Geology 19, 24–27 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, B., Kenneth MacLeod, G. & Ward, P. Rapid change in strontium isotopic composition of sea water before the Cretaceous/Tertiary boundary. Nature 351, 644–647 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/351644a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/351644a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Reorganization of deep ocean circulation accompanying a Late Cretaceous extinction event
Nature (1996)
-
Marine isotope evolution
Nature (1992)
-
Strontium isotopes at K/T boundary
Nature (1992)
-
Acid rain at the K/T boundary
Nature (1991)