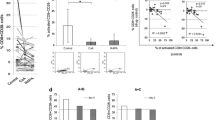
Abstract
ONE mechanism by which the immune system develops the ability to discriminate self from nonself is the deletion of autoreactive T-cell clones during thymic maturation1–4. The drug cyclosporin A (CsA) has been shown to interfere with this process, allowing the escape of normally 'forbidden' T-cell clones5,6 and the appearance of autoimmune disease7–10. Recently, it has been demonstrated that immature thymocytes undergo programmed cell death (apoptosis) upon activation via the T-cell receptor11. A similar phenomenon of activation-induced cell death (AICD) has been observed in T-cell hybridomas12,13. Here we show that AICD in T-cell hybridomas in vitro and in thymocytes in vivo is blocked by CsA. Thus, clonal deletion may involve AICD when self-reactive, immature T cells are induced by self antigen, and CsA may cause autoimmunity by interfering with this process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kappler, J. W. et al. Cell 49, 263–271 (1987).
Kappler, J. W., Staerz, U., White, J. & Marrack, P. Nature 332, 35–40 (1988).
MacDonald, H. R. et al. Nature 332, 40–45 (1988).
Kisielow, P., Bluthmann, H., Staerz, U. D., Steinmetz, M. & von Boehmer, H. Nature 333, 742–746 (1988).
Gao, E.-K., Lo, D., Cheney, R., Kanagawa, O. & Sprent, J. Nature 336, 176–179 (1988).
Jenkins, M. K., Schwartz, R. H. & Pardoll, D. M. Science 241, 1655–1658 (1988).
Glazer, A., Tutschha, P. J., Farmer, E. R. & Santos, G. W. J. exp. Med. 158, 1–8 (1983).
Hess, A. D. et al. J. exp. Med. 161, 718–730 (1985).
Cheney, R. T. & Sprent, J. Transplant proc. 17, 528–530 (1985).
Sakaguchi, S. & Sakaguchi, N. J. exp. Med. 167, 1479–1485 (1988).
Smith, C. A., Williams, G. T., Kingston, R., Jenkinson, E. J. & Owen, J. J. Nature 337, 181–184 (1989).
Ashwell, J. D., Cunningham, R. E., Noguchi, P. D. & Hernandez, D. J. exp. Med. 165, 173–194 (1987).
Mercep, M., Bluestone, J. A., Noguchi, P. D. & Ashwell, J. D. J. Immun. 140, 324–335 (1988).
Shevach, E. M. A. Rev. Immun. 3, 397–424 (1985).
Fotedar, A. et al. J. Immun. 135, 3028–3033 (1985).
Mossmann, T. R. J. Immun. meth. 65, 55–63 (1983).
Leo, O., Foo, M., Sachs, D. H., Samelson, L. E. & Bluestone, J. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 1374–1378 (1987).
Butcher, E. C. & Ford, W. L. in Handbook of Experimental Immunology Vol. 2, Cellular Immunology (eds Weir, D. M., Herzenberg, L. A., Blackwell, C. & Herzenberg, L. A.) 57.13–57.15. (Blackwell, Oxford, 1986).
Wyllie, A. H. Arch. Toxicol. 11, (Suppl.) 3–10 (1987).
Walker, N. I., Harmon, B. V., Gobe, G. C. & Kerr, J. F. R. Meth. Achieve. exp. Path. 13, 18–54 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, Y., Sahai, B. & Green, D. Cyclosporin A inhibits activation-induced cell death in T-cell hybridomas and thymocytes. Nature 339, 625–626 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/339625a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/339625a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Identification of ITPR1 gene as a novel target for hsa-miR-34b-5p in non-obstructive azoospermia: a Ca2+/apoptosis pathway cross-talk
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Recent advances in cancer immunotherapy
Discover Oncology (2021)
-
FAS-ligand regulates differential activation-induced cell death of human T-helper 1 and 17 cells in healthy donors and multiple sclerosis patients
Cell Death & Disease (2015)
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors prevent activation-induced cell death and promote anti-tumor immunity
Oncogene (2015)
-
Thy28 protects against anti-CD3-mediated thymic cell death in vivo
Apoptosis (2015)