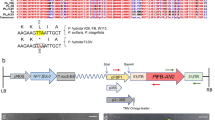
Abstract
Petunia hybrida is one of the classical subjects of investigation in plants in which the pathway of anthocyanin biosynthesis has been analysed genetically and biochemically. In petunia cyanidin- and delphinidin-derivatives, but no pelargonidin-derivatives are produced as pigments. This is due to the substrate specificity of the dihydroflavonol 4-reductase of petunia, which cannot reduce dihy-drokaempferol. The petunia mutant RL01, which accumulates dihydrokaempferol, shows no flower pigmentation. RL01 served as a recipient for the transfer of the A1 gene of Zea mays encoding dihydroquercetin 4-reductase, which can reduce dihydrokaempferol and thereby provided the intermediate for pelargonidin biosynthesis. Transformation of RL01 with a vector p35Al, containing the A1 -complementary DNA behind the 35S promotor leads to red flowers of the pelargonidin-type. Thus a new flower pigmentation pathway has been established in these plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Heller, W., Forkmann, G., Britsch, L. & Grisebach, H. Planta 165, 284-287 (1985). 2. Forkmann, G. & Ruhnau, B. Z. Naturforsch. 42c, 1146-1148 (1987). 3. Cornu, A., Paynot, M. & Touvin, H. Phytochemistry 13, 2022 (1974). 4. Stotz, G., de Vlaming, P., Wiering, H., Schramm, A. W. & Forkmann, G. Theor. appl. Genet. 70, 300-305 (1985). 5. Stotz, G. thesis, Univ. Tubingen (1983). 6. Forkmann, G., de Vlaming, P., Spribille, R. & Schram, A. W. Z. Naturforsch. 41c, 179-186 (1986). 7. Wiering, H. & de Vlaming, P. in Petunia Monograph (ed. Sink) 49-67 (Springer, Berlin, 1984). 8. Schwarz-Sommer, Z. et al. EMBO J. 2, 287-294 (1987). 9. Reddy, A. R., Britsch, L., Salamini, F., Saedler, H. & Rohde, W. PI. Sci. 52, 7-12 (1987). 10. Meyer, P., Walgenbach, E., Bussmann, K., Hombrecher, G. & Saedler, H. Molec. gen. Genet. 201, 513-518 (1985). 11. Harborne, J. B. Comparative Biochemistry of the Flavonoids (Academic, London & New York, 1967). 12. Main, R. et al. Molec. gen. Genet. 199, 161-168 (1985). 13. Shilito, R. D., Paszkowski, I. & Potrykus, I. PL Cell Rep. 2, 244-247 (1983). 14. Binding, H. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 74, 327-356 (1974). 15. Murashige, T., Skoog, F. Physiol. PI. 15, 473-497 (1962). 16. Logemann, J., Schell, J. & Wilmitzer, L. Analyt. Biochem. 163, 16-20 (1987). 17. Feinberg, A. P. & Vogelstein, R. Analyt. Biochem. 132, 6-13 (1983). 18. Feinberg, A. P. & Vogelstein, R. Analyt. Biochem. 137, 266-267 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, P., Heidmann, I., Forkmann, G. et al. A new petunia flower colour generated by transformation of a mutant with a maize gene. Nature 330, 677–678 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/330677a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/330677a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The effect of different LED wavelengths on the components and biosynthesis of isoflavonoid in sprout Astragalus membranaceus
Protoplasma (2024)
-
Transcriptional networks orchestrating red and pink testa color in peanut
BMC Plant Biology (2023)
-
Applications of CRISPR/Cas9 Technology in Ornamental Plants
Plant Molecular Biology Reporter (2023)
-
Cloning and functional analysis of GhDFR1, a key gene of flavonoid synthesis pathway in naturally colored cotton
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
Physiological changes besides the enhancement of pigmentation in Petunia hybrida caused by overexpression of PhAN2, an R2R3-MYB transcription factor
Plant Cell Reports (2023)