Abstract
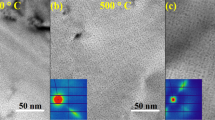
Microstructural changes induced in metals by ion bombardment have important implications for technology (see, for example, refs 1–3). Helium irradiation can result in the formation of small (∼2nm diameter) helium bubbles in high concentration (∼1025 m–3), ordered on a superlattice. Current theories are all directed towards explaining the formation of a superlattice having the same alignment as the crystal lattice of the metal—the matrix or m orientation. In the face-centred-cubic metal copper, although there was evidence in previous work that some domains4 in the bubble array were in orientations other than m (ref. 5), it may have been assumed that the proportion of such domains was small. Here we report new results that show that a high proportion of the ordered bubble array is in domains that have orientations different from m. We propose that a new mechanism, based on the spatial characteristics of the stress field around an overpressurized bubble, must play a dominant role in the later stages of bubble ordering.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donnelly, S. E. Radiat. Effects 90, 1–47 (1985).
Dearnaley, G. Surf. Engng 2, 213–221 (1986); Nucl Instrum. Meth. B7/8, 158–165 (1985).
Johnson, P. B. & Armstrong, T. R. Nucl. Instrum. Meth. 148, 85–92 (1978).
Johnson, P. B. & Mazey, D. J. Nature 276, 595–596 (1978).
Johnson, P. B. & Mazey, D. J. J. nucl. Mater. 127, 30–46 (1985).
Dubinko, V. I., Slezov, V. V., Tur, A. V. & Yanovsky, V. V. Radiat. Effects 100, 85–104 (1986).
Stoneham, A. M. in Harwell Unclassified Rep. No. AERE-R7934, 319–329 (1975).
Krishan, K. Radial. Effects. 66, 121–155 (1982).
Evans, J. H. J. nucl. Mater. 132, 147–155 (1985).
Evans, J. H. & Mazey, D. J. J. nucl. Mater. 138, 176–184 (1986).
Evans, J. H. J. nucl. Mater. 76/77, 228–234 (1978).
Barnes, R. S. & Mazey, D. J. Acta metall. 11, 281–286 (1963).
Shiraishi, K., Hishinuma, A. & Katano, Y. Radiat. Effects 21, 161–164 (1974).
Johnson, P. B. & Jones, W. R. J. nucl. Mater. 120, 125–132 (1984).
Johnson, P. B. in 4th Ann. Solid Slate Phys. Mtg Aust./NZ Inst. Phys. (Phys. Rpt 1/82, Victoria Univ., Wellington, 1982).
Bullough, R. & Newman, R. C. Phil. Mag. 5, 921–926 (1960).
Eer Nisse, E. P. & Picraux, S. T. J. appl. Phys. 48, 9–17 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Johnson, P., Malcolm, A. & Mazey, D. Importance of stress in bubble ordering in the helium gas-bubble superlattice in copper. Nature 329, 316–318 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/329316a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/329316a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Large bubble-like features ordered on a macrolattice in helium-implanted gold
Nature (1990)
-
Novel model for cavity lattices
Nature (1987)