Abstract
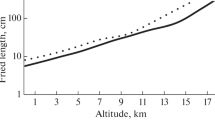
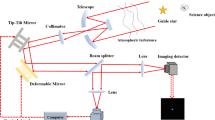
Atmospheric turbulence severely limits the resolution of ground-based astronomical telescopes. Under good seeing conditions at the best observatory sites, resolution at visible wavelengths is typically limited to about 1 arc s. During the past 15 years, adaptive optical systems with electrically deformable mirrors have been developed to compensate for turbulence1,2. Unfortunately, these systems require bright reference sources adjacent to the object of interest and can only be used to observe the brightest stars. Foy and Labeyrie3 were the first to suggest that lasers could be used to create artificial guide stars that might be suitable in controlling an adaptive imaging system. We have recently extended this concept in two ways. First, we have identified the key engineering parameters that optimize the performance of a laser-guided imaging system. Second, on the nights of 21 and 22 January 1987, we conducted experiments at the Mauna Kea Observatory on the island of Hawaii to test the feasibility of using a laser to generate an artificial guide star in the mesospheric sodium layer. Here we describe both the engineering calculations and the results of our first experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
1. Hardy, J. W. Proc. Inst. elect. Electron. Engrs 66, 651–697 (1978). 2. Pearson, J. E., Freeman, R. H. & Reynolds, H. C. Jr in Applied Optics and Optical Engineering Vol. 7 (eds Shannon, R. & Wyant, J.) 245–340 (Academic, New York, 1979). 3. Foy, R. & Labeyrie, A. Astr. Astrophys. 152, L29–L31 (1985). 4. Fried, D. L. J. opt. Soc. Am. 56, 1372–1379 (1966). 5. Thompson, L. A. & Ryerson, H. H. Proc. SPIE Conf. Instr. Astron. V, 455, 560–568 (1984). 6. Gardner, C. S., Voelz, D. G., Sechrist, C. F. Jr & Segal, A. C. /. geophys. Res. 91,13659–13673 (1986). 7. Megie, G., Bos, F., Blamont, J. E. & Chanin, M. L. Planet. Space Sci. 26, 27–35 (1977). 8. Hlivak, R. J., Pilcher, C. B., Howell, R. R., Colucci, A. J. & Henry, J. P. Proc. SPIE Conf. Instr. Astr. IV. 331, 96–103 (1982). 9. Oke, J. B. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 27, 21–35 (1974). 10. Stone, R. P. S. Astrophys. J. 218, 767–769 (1977). 11. Gardner, C. S. & Voelz, D. G. J. geophys. Res. 92, 4673–4694 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, L., Gardner, C. Experiments on laser guide stars at Mauna Kea Observatory for adaptive imaging in astronomy. Nature 328, 229–231 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/328229a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/328229a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Compact and high reliable frequency-stabilized laser system at 589 nm based on the distributed-feedback laser diodes
Applied Physics B (2021)
-
Investigation of return photons from sodium laser beacon excited by a 40-watt facility-class pulsed laser for adaptive optical telescope applications
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Remote sensing of geomagnetic fields and atomic collisions in the mesosphere
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Atmospheric and adaptive optics
The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review (2014)
-
Millimeter-wave atmospheric turbulence measurements: Instrumentation, selected results, and system effects
International Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves (1997)