Abstract
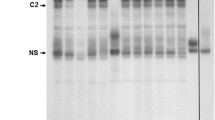
Proteins binding to specific regions of DNA with high affinity frequently govern or regulate reactions at the gene level1–8. We have identified a high-affinity binding site in the immunoglobulin μ gene that binds a specific nuclear protein, and have now characterized it fully using nuclear factor 1 (NF-1), a protein purified from the nuclei of HeLa cells9,10 and required for the in vitro replication of adenovirus (Ad) DNA9–12. NF-1 protects a 25-base pair (bp) double-stranded segment of DNA which shares a consensus sequence, 5′ TGGA/CNNNNNGCCAA 3′, with similar binding sites in the Ad-5 terminal repeat10–12 and the human c-myc gene13. Although this site differs from the enhancer region13–16, a biological function is suggested by the fact that it is DNase I hypersensitive in immunoglobulin-producing lymphoblastoid cells. The binding site for the NF-1 protein in the μ gene, by analogy with the site in the Ad-5 terminal repeat, may represent one component of a cellular origin of replication; alternatively, it may be responsible for the activation of the chromatin in this region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilbert, W., Maizels, N. & Maxam, A. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 38, 845–855 (1974).
Maniatis, T. et al. Cell 5, 109–113 (1975).
Dynan, W. S. & Tjian, R. Cell 35, 79–87 (1983).
Jones, K. A. & Tjian, R. Cell 36, 155–162 (1984).
Compton, J. G., Schrader, W. T. & O'Malley, B. W. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 16–20 (1983).
Karin, M. et al. Nature 308, 513–519 (1984).
Renkawitz, R., Schutz, G. von der Ahe, D. & Beato, M. Cell 37, 503–510 (1984).
Chandler, V. L., Maler, B. A. & Yamamoto, K. R. Cell 33, 489–499 (1983).
Nagata, K., Guggenheimer, R. A., Enomoto, T., Lichy, J. H. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 6438–6442 (1982).
Rawlins, D. R., Rosenfeld, P. J., Wides, R. J., Challberg, M. D. & Kelly, T. J. Jr Cell 37, 309–319 (1984).
Nagata, K., Guggenheimer, R. A. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 6177–6181 (1983).
Guggenheimer, R. A., Stillman, B. W., Nagata, K., Tamanoi, F. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 3069–3073 (1984).
Siebenlist, U., Hennighausen, L., Battey, J. & Leder, P. Cell 37, 381–391 (1984).
Hayday, A. et al. Nature 307, 334–340 (1984).
Rabbitts, T. H., Hamlyn, P. H. & Baer, R. Nature 306, 760–765 (1983).
Bannerji, J., Olson, L. & Schaffner, W. Cell 33, 729–740 (1983).
Taub, R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 7837–7841 (1982).
Leder, P. et al. Science 222, 765–771 (1983).
Battey, J. et al. Cell 34, 779–789 (1983).
Taub, R. et al. Cell 36, 339–348 (1984).
Riggs, A. D., Bourgeois, S. & Cohn, M. J. molec. Biol. 53, 401–417 (1970).
Jack, R. S., Gehring, W. J. & Brack, C. Cell 24, 321–333 (1981).
Borgmeyer, U., Nowock, J. & Sippel, A. E. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 4295–4311 (1984).
Pabo, C. & Lewis, A. Nature 298, 443–447 (1982).
Shermoen, A. W. & Beckendorf, S. K. Cell 29, 601–607 (1982).
Emerson, B. M. & Felsenfeld, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 95–99 (1984).
Gronostajski, R. M., Nagata, K. & Hurwitz, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 4013–4017 (1984).
Lewin, B. M. Gene Expression 2 2nd edn (Wiley, New York, 1980).
Leder, P. Sci. Am. 246(5), 102–115 (1982).
Shimizu, A. & Honjo, T. Cell 36, 801–803 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hennighausen, L., Siebenlist, U., Danner, D. et al. High-affinity binding site for a specific nuclear protein in the human IgM gene. Nature 314, 289–292 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1038/314289a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/314289a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Molecular Regulation of JC Virus Tropism: Insights into Potential Therapeutic Targets for Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy
Journal of Neuroimmune Pharmacology (2010)
-
A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs
Nature (1988)
-
Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication
Nature (1986)
-
Putative repressor binding sites in the regions mediating transcriptional control of viral and cellular genes
Bioscience Reports (1985)