Abstract
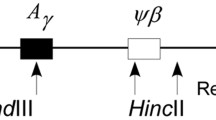
It has been suggested that there is a close linkage between specific restriction fragment polymorphism patterns, defined as haplotypes, in the β-globin gene cluster and specific mutations in Mediterranean people with thalassaemia1. This association formed the basis of a strategy for the efficient characterization of β-thalassaemia mutations from the DNA sequence of one or two β-thalassaemia genes derived from each haplotype in each ethnic group. Subsequently, Robertson and Hill argued that this strategy greatly underestimates the number of mutations on haplotypes which are frequent among normal chromosomes2. We have therefore now analysed the proposed association and strategy quantitatively by the use of oligonucleotide hybridization and direct restriction analysis. Our results suggest that: (1) the association of specific haplotypes with specific mutations is high, but not invariant; (2) a different β-thalassaemia mutation has arisen within each haplotype in Mediterraneans; and (3) mutation spread from one haplotype to another occurs mainly through meiotic recombination within a 9-kilobase region 5′ to the β-globin gene
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orkin, S. H. et al. Nature 296, 627–631 (1982).
Robertson, A. & Hill, W. G. Nature 301, 176–177 (1983).
Antonarakis, S. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 79, 137–141 (1982).
Kazazian, H. H. Jr et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 36, 212–217 (1984).
Antonarakis, S. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 81, 1154–1158 (1984).
Kazazian, H. H. Jr et al. EMBO J. (in the press).
Cheng, T.-c. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 81, 593–596 (1984).
Wallace, R. B. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 9, 3647–3656 (1981).
Spritz, R. A. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 78, 2455–2459 (1981).
Moschonas, N. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 9, 4391–4401 (1981).
Trecartin, R. F. et al. J. clin. Invest. 68, 1012–1017 (1981).
Treisman, R. A. et al. Cell 29, 903–911 (1982).
Kazazian, H. H. Jr et al. Am. J. hum. Genet. 35, 1028–1033 (1983).
Maeda, N., Bliska, J. B. & Smithies, O. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 80, 5012–5016 (1983).
Antonarakis, S. E. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 81, 853–856 (1984).
Arous, N. et al. FEBS Lett. 147, 247–250 (1983).
Dobkin, C. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 80, 1184–1188 (1983).
Southern, E. M. et al. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975).
Conner, B. J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. sci. U.S.A. 80, 278–282 (1983).
Orkin, S. H., Markham, A. F. & Kazazian, H. H. Jr J clin. Invest. 71, 775–779 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazazian, H., Orkin, S., Markham, A. et al. Quantification of the close association between DNA haplotypes and specific β-thalassaemia mutations in Mediterraneans. Nature 310, 152–154 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/310152a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/310152a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Gradient of distribution in Europe of the major CF mutation and of its associated haplotype
Human Genetics (1990)
-
Intrinsic potential for high fetal hemoglobin production in a Druze family with β-thalassemia is due to an unlinked genetic determinant
Human Genetics (1990)
-
The frequency and origin of the sickle cell mutation in the district of Coruche/Portugal
Human Genetics (1989)
-
Mutation analysis of β-thalassemia genes in a German family reveals a rare transversion in the first intron
Human Genetics (1989)
-
The peculiar spectrum of ?-thalassemia genes in Tunisia
Human Genetics (1988)