Abstract
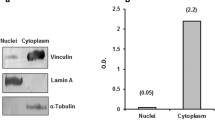
The localization of vinculin, an actin-binding protein1,2 of molecular weight 130,000 (130K) at a variety of cytoskeletal-associated membrane specializations including the zonula adherens of intestinal epithelial cells3, fascia adherens of intercalated discs3, focal adhesion plaques in fibroblasts4,5, and costameres (sarcolemmal domains in periodic register with the I-bands of subjacent myofibrils) in cardiac and skeletal muscle6, suggests that vinculin could link actin to cell membranes. This hypothesis is supported by immuno-ultrastructural studies which show that vinculin is closely apposed to the plasma membrane at sites where actin-containing microfilaments terminate3,7. But since vinculin has the solubility properties of a peripheral membrane protein4, there would also need to be an integral membrane component to which it bound to link actin filaments to the plasma membrane. Our efforts to identify the presumed membrane binding site for vinculin resulted instead in the detection of a 150K protein which we term meta-vinculin (Greek meta among, with; in the sense of closely related to), that is immunologically related to 130K vinculin. Unlike vinculin, meta-vinculin has the solubility properties of an integral membrane protein. Given its location within the cell, it is possible that meta-vinculin is an integral membrane anchor protein for actin filaments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jockusch, B. M. & Isenberg, G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 3005–3009 (1981).
Wilkins, J. A. & Lin, S. Cell 28, 83–90 (1982).
Geiger, B. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 77, 4127–4131 (1980).
Geiger, B. Cell 18, 193–205 (1979).
Burridge, K. & Feramisco, J. R. Cell 19, 587–595 (1980).
Pardo, J. V., Siliciano, J. D. & Craig, S. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (submitted).
Tokuyasu, K. T. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 7619–7623 (1981).
Yu, J. & Steck, T. L. J. supramolec. Struct. 1, 220–232 (1973).
Yu, J., Fischman, D. A. & Steck, T. L. J. supramolec. Struct. 1, 233–248 (1973).
Feramisco, J. R. & Burridge, K. J. biol. Chem. 255, 1194–1199 (1980).
Craig, S. W., Lancashire, C. L. & Cooper, J. J. Meth. Enzym. 85, 316–321 (1982).
Towbin, H., Staehlin, T. & Gordon, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76, 4350–4354 (1979).
Olmstead, J. B. J. biol. Chem. 256, 11955–11957 (1981).
Rogers, J. et al. Cell 20, 303–312 (1980).
Feramisco, J. R., Burridge, K., Smart, J. E. & Thomas, G. P. J. Cell Biol. 91, 292a (1981).
Sobue, K., Muramoto, Y., Fujita, M. & Kakiuchi, S. Biochem. International 2, 469–476 (1981).
Helenius, A. & Simons, K. Biochim. biophys. Acta 415, 29–79 (1974).
Adair, W. S., Jurivich, D. & Goodenough, V. W. J. Cell Biol. 79, 281–285 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siliciano, J., Craig, S. Meta-vinculin—a vinculin-related protein with solubility properties of a membrane protein. Nature 300, 533–535 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1038/300533a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/300533a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Molecular domain structure of porcine vinculin and metavinculin
Protoplasma (1988)
-
Interaction of the cytoskeleton with the plasma membrane
The Journal of Membrane Biology (1987)
-
Metavinculin and vinculin from mammalian smooth muscle: Bulk isolation and characterization
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1987)
-
Diacylglycerol in large α-actinin/actin complexes and in the cytoskeleton of activated platelets
Nature (1985)
-
The thin filaments of smooth muscles
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (1985)