Abstract
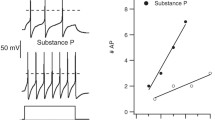
Dopamine (DA) is an important neurotransmitter or neuromodulator in the mammalian nervous system. As such, it is implicated in the aetiology and therapy of various disease conditions—for example, Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, Huntington's disease and tardive dyskinesia. However, only limited electrophysiological information is presently available concerning dopamine receptors in the mammalian nervous system1, and there are only three reports2–4 in which intracellular techniques have successfully recorded the action of DA on individual central neurones. In all cases, DA depolarised the respective neurones. In the periphery, DA is reported to hyperpolarise superior cervical ganglia5–9. However, this hyperpolarisation has been shown to be due to activation of α-adrenoreceptors and not to a response of DA on a DA receptor8,9. Peripheral DA actions have also been described presynaptically10,11, but are difficult to study electrophysiologically for technical reasons. As a result, little is known at the membrane level about the effects of drugs thought to modulate or interact with DA receptors. In the present report, we describe a depolarising action for DA on the cat dorsal root ganglion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krnjevic, K. in Adv. Neurol. 9, 13–24 (1975).
Kitai, S. T., Sugimori, M. & Kocsis, J. D. Expl Brain Res. 24, 351–363 (1976).
Bernardi, G., Marciani, M. G., Morocutti, C., Pavone, F. & Stanzione, P. Neurosci. Lett., 8, 235–240 (1978).
Herrling, P. L., Hull, C. D. & Buchwald, N. A. Neurosci. Lett. 9, suppl. 1, S258 (1978).
Libet, B. Fedn Proc. 29, 1945–1956 (1970).
Dun, N. & Karczmar, A. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4029–4032 (1978).
Nakamura, J. Kurume med. J. 25, 241–253 (1978).
Brown, D. A. & Caulfied, M. P. Br. J. Pharmac. 65, 435–445 (1979).
Cole, A. & Shinnick-Gallagher, P. Neurosci. Abstr. 9, 2485 (1979).
Dun, N. & Nishi, S. J. Physiol., Lond. 239, 155–164 (1974).
Steinsland, O. S. & Hieble, J. P. Science 199, 443–445 (1978).
Gallagher, J. P., Higashi, H. & Nishi, S. J. Physiol., Lond. 275, 263–282 (1978).
Nishi, S., Minota, S. & Karzzmar, A. G. Neuropharmacology 13, 215–216 (1974).
Nicoll, R. A. J. Physiol., Lond. 283, 121–132 (1978).
Feltz, P. & Rasminsky, M. Neuropharmacology 13, 553–563 (1974).
Janssen, P. A. in Neurophsychopharmacology Vol. 4 (eds Bente, D. & Bardley, P.B.) 151 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1965).
Maruyama, S. & Kawasaki, T. Jap. J. Pharmac. 25, 209–213 (1975).
Myers, P. R., Livengood, D. R. & Shain, W. J. cell. Physiol. 91, 103–118 (1977).
Nishi, S., Soeda, H. & Koketsu, K. Life Sci. 8, 33–42 (1969).
Higashi, H. Nature 267, 448–450 (1977).
Wallis, D. I. & North, R. A. Neuropharmacology 17, 1023–1028 (1978).
Phillis, J. W. & Kirkpatrick, J. R. Gen. Pharmac. 10, 115–119 (1979).
Commissiong, J. W. & Neff, N. H. Biochem. Pharmac. 28, 1569–1573 (1979).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallagher, J., Inokuchi, H. & Shinnick-Gallagher, P. Dopamine depolarisation of mammalian primary afferent neurones. Nature 283, 770–772 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/283770a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/283770a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Inhibition of Tetrodotoxin-Resistant Sodium Current in Dorsal Root Ganglia Neurons Mediated by D1/D5 Dopamine Receptors
Molecular Pain (2013)
-
Analysis of two types of dopaminergic responses of neurons of the spinal ganglia of rats
Neuroscience and Behavioral Physiology (1991)
-
Dopamine and serotonin effects on neurons of dorsal root ganglion isolated from rats
Neurophysiology (1990)
-
Depolarizing effects of dopamine on the primary afferent fibers of a segment isolated from the spinal cord of newborn rats
Neurophysiology (1988)
-
Atypical responses ofHelix pomatia neurons to dopamine
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (1983)