Abstract
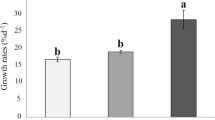
RIVER drainage from mineral-bearing and industrialised regions has produced elevated concentrations of heavy metals in several parts of the coastal waters around the UK, including Liverpool Bay1,2, Cardigan Bay1, the Bristol Channel1–3, off the mouth of the River Tees4 and in the Firth of Clyde5. Little attention has been paid, however, to the possibility that the presence of the metals might be affecting the planktonic marine life of these sea areas. Phytoplankton represent the basic food resource on which the majority of marine animals and fish directly or indirectly depend, and it is thus conceivable that inhibition of their growth by toxic metals could have repercussions throughout the local marine food webs. We are investigating the role of trace quantities of both biologically beneficial and toxic substances in regulating the ‘quality’ of seawater, that is, its capacity to support and maintain, through photosynthesis, the production of living matter from the inorganic nutrients present in the water. As part of this research programme, we have examined how carbon fixation rates in natural populations of phytoplankton are affected by zinc concentrations encompassing those observed in the areas mentioned. Although zinc is a component of many enzyme systems6 and therefore essential for the growth of phytoplankton7, it becomes toxic if present greatly in excess of their basic requirements. We report here data which suggest that phytoplankton growth could be depressed by the zinc concentrations present in some British coastal waters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah, M. I., Royle, L. G. & Morris, A. W. Nature 235, 158–160 (1972).
Preston, A., Jefferies, D. F., Dutton, J. W. R., Harvey, B. R. & Steele, A. K. Envir. Pollut. 3, 69–82 (1972).
Abdullah, M. I. & Royle, L. G. J. mar. biol. Ass. 54, 581–597 (1974).
Dutton, J. W. R., Jefferies, D. F., Folkard, A. R. & Jones, P. G. W. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 4, 135–138 (1973).
Halcrow, W., Mackay, D. W. & Thornton, I. J. mar. biol. Ass. 53, 721–739 (1973).
Bowen, H. J. M. Trace Elements in Biochemistry, 119–134 (Academic, London, 1966).
O'Kelley, J. C. in Algal Physiology and Biochemistry (ed. Stewart, W. D. P.) 610–635 (Blackwell, Oxford, 1974).
Steemann-Nielsen, E. J. Cons. Perm. int. Explor. Mer. 18, 117–140 (1952).
Davies, A. G. Adv. mar. Biol. 15, 381–508 (1978).
Braek, G. S., Jensen, A. & Mohus, A. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 25, 37–50 (1976).
Foster, P. & Morris, A. W. Estuar. Cstl. Mar. Sci. 2, 283–290 (1974), Envir. Pollut. 7, 121–132 (1974).
Sunda, W. & Guillard, R. R. L. J. mar. Res. 34, 511–529 (1976).
Jensen, A., Rystad, B. & Melsom, S. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 15, 145–157 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DAVIES, A., SLEEP, J. Photosynthesis in some British coastal waters may be inhibited by zinc pollution. Nature 277, 292–293 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1038/277292a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/277292a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Effects of zinc and iron on the abundance of Microcystis in Lake Taihu under green light and turbulence conditions
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2022)
-
Interaction of Zn2+ with the donor side of Photosystem II
Photosynthesis Research (1991)
-
Inhibition of photosynthesis by heavy metals
Photosynthesis Research (1985)
-
Interactive effects of metals and humus on marine phytoplankton carbon uptake
Nature (1983)
-
Characteristic deformities in tubificid oligochaetes inhabiting polluted bays of Lake Vänern, Southern Sweden
Hydrobiologia (1983)