Abstract
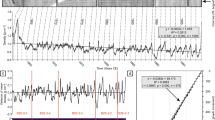
THE skeletal aragonite deposited by scleractinian reef corals is characterised by alternating bands of high and low density carbonate that are concordant with the growth surface of the colony. These density variations, which are readily observed by X-radiographic examination of 5–10 mm thick sections of the corallum cut parallel to the axis of growth, are annual in periodicity, such that one high density band plus one adjacent low density band represent the skeletal increment formed over one calendar year1–4. Skeletal X radiography is a powerful tool for studying both modern and fossil corals, for in addition to providing a wealth of growth rate data from specimens that grew undisturbed for many years in their natural habitat on the reef, valuable information about the coral itself and about the environment in which the coral lived can be obtained. As Buddemeier5 points out, density banding in reef corals can not only yield physiological and ecological information about these marine organisms, but also help to unlock the record of long term environmental conditions that is embodied in a coral skeleton. Reef corals, for example, are effective samplers of certain important radionuclides6.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Knutson, D. K., Buddemeier, R. W., and Smith, S. V., Science, 177, 270–272 (1972).
Macintyre, I. G., and Smith, S. V., in Proc. second Int. Symp. Coral Reefs, Australia, 2, 277–287 (1974).
Moore, W. S., and Krishnaswami, S., ibid., 2, 269–276 (1974).
Dodge, R. E., and Thomson, J., Earth planet. Sci. Lett., 23, 313–322 (1974).
Buddemeier, R. W., in Proc. second Int. Symp. Coral Reefs, Australia, 2, 259–267 (1974).
Knutson, D. K., and Buddemeir, R. W., Int. Atom. Energy Agency (Vienna) Publ. SM-158/49, 735–746 (1973).
Buddemeier, R. W., Maragos, J. E., and Knutson, D. K., J. exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol., 14, 179–200 (1974).
Buddemeier, R. W., and Kinzie, R. A., Proc. Newcastle Interdisciplinary Conf. Biological Clocks and Changes in the Earth's Rotation (Wiley, in the press).
Weber, J. N., and White, E. W., Geol. Soc. Am. Abstr. with Programs, 6, (7) 1003 (1974).
Weber, J. N., and White, E. W., J. Paleobiol, 1 (in the press).
Weber, J. N., and Woodhead, P. M. J., J. geophys. Res., 77, 463–473 (1972).
Weber, J. N., and Woodhead, P. M. J., Mar. Biol., 15, 293–297 (1972).
Weber, J. N., and Woodhead, P. M. J., Chem. Geol., 6, 93–117 (1970).
Snedecor, G. W., Statistical Methods, 429–432 (Iowa State University Press, 1956).
Weber, J. N., and White, E. W., Mar. Biol., 26, 353–359 (1974).
Weber, J. N., and White, E. W., Proc. seventh Caribbean Geol. Conf., Guadeloupe (in the press).
Weber, J. N., and Raup, D. M., Geochim. cosmochim. Acta, 30, 681–736 (1966).
Deines, P., Int. J. Mass Spectrom. Ion Phys., 4, 283–295 (1970).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
WEBER, J., DEINES, P., WHITE, E. et al. Seasonal high and low density bands in reef coral skeletons. Nature 255, 697–698 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255697a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255697a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Quantifying skeletal density at high temporal resolution in massive scleractinian corals by using two-dimensional grid-scanning gamma densitometry
Geo-Marine Letters (2022)
-
Environmental impact on the mechanical properties of Porites spp. corals
Coral Reefs (2021)
-
Historical photographs revisited: A case study for dating and characterizing recent loss of coral cover on the inshore Great Barrier Reef
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Seasonal variations in the stable isotopic composition and the skeletal density pattern of the coral Porites lobata (Gulf of Eilat, Red Sea)
Marine Biology (1992)
-
Variation in coral growth rates with depth at Discovery Bay, Jamaica
Coral Reefs (1985)