Abstract
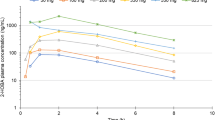
VITAMIN C (ascorbic acid) is taken by many individuals in very large doses and there has been some concern about possible adverse effects of such regimens. It has been found that vitamin C is metabolised in part to ascorbic acid sulphate in man1. Sulphate formation is also an important pathway for the biotransformation of phenolic drugs2. This pathway is, however, of limited capacity in man3 (and in many species of animals) and is therefore subject to saturation and competitive inhibition. Such mutual inhibition by two or more substrates is caused by the limited availability of sulphate and can be overcome by concomitant administration of sulphate or a sulphate donor3. Studies in man have demonstrated competitive inhibition of sulphate formation between acetaminophen and salicylamide, two widely used analgesics and antipyretics, and the prevention of this inhibition by concomitant administration of the sulphate donor L-cysteine4. We now report the results of a study which shows that concomitant administration of vitamin C and salicylamide causes a decrease in the conversion of the latter to salicylamide sulphate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, E. M., Hammer, D. C., March, S. C., Tolbert, B. M., and Canham, J. E., Science, 173, 826–827 (1971).
Williams, R. T., Detoxification Mechanisms, second ed., ch. 9, 279–282 (Chapman and Hall, London, 1959).
Levy, G., and Matsuzawa, T., J. Pharmac. exp. Ther., 156, 285–293 (1967).
Levy, G., and Yamada, H., J. Pharm. Sci., 60, 215–221 (1971).
Hunt, J. N., and Knox, M. T., J. Physiol., Lond., 222, 187–208 (1972).
Kubler, W., and Gehler, J., Int. Z. Vitaminforsch., 40, 442–445 (1970).
Physicians Desk Reference, 28th ed., 1574–1578 (Medical Economics, Oradell, New Jersey, 1974).
Levy, G., Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 179, 32–42 (1971).
George, C. F., Blackwell, E. W., and Davies, D. S., J. Pharm. Pharmac., 26, 265–267 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HOUSTON, J., LEVY, G. Modification of drug biotransformation by vitamin C in man. Nature 255, 78–79 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/255078a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/255078a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
The influence of nutrition on the systemic availability of drugs
Klinische Wochenschrift (1987)
-
Arzneimittel und Vitaminversorgung
Zeitschrift für Ernährungswissenschaft (1978)
-
Wechselwirkung zwischen Ernährung und Arzneimitteln
Zeitschrift für Ernährungswissenschaft (1976)
-
Competition for sulphate during detoxification in the gut wall
Nature (1975)