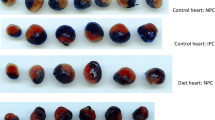
Abstract
IN physiological concentrations, circulating long chain free fatty acids (FFA) can inhibit the myocardial oxidation of glucose and are the preferred fuel of the heart in the fasted state1,2. In sufficiently high concentrations, fatty acids as the only fuel can have toxic effects on the normal perfused rat heart3. The mechanisms involved in fatty acid toxicity may include the intracellular accumulation of products of fatty acid metabolism such as acyl CoA (ref. 4), which inhibits the transfer of ATP from sites of synthesis in the mitochondria to sites of utilisation in the cytoplasm. Thus, enhanced rates of FFA metabolism could be expected to aggravate myocardial infarction, in which there is a loss of ATP in the poorly perfused tissue predominantly supplied by the occluded artery5. As an intracellular ATP deficiency is postulated to be a factor promoting release of enzymes6, increased provision of FFA to the heart should accelerate enzyme release from infarcting heart tissue. Conversely, if the rate of accumulation of FFA breakdown products were decreased by the additional provision of glucose or glucose plus insulin to promote intracellular esterification of FFA, then the rate of enzyme release should be decreased. Increased provision of glucose could also result in increased production of anaerobic ATP which could be of importance in promoting the survival of the oxygen-limited myocardium7.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shipp, J. C., Opie, L. H., and Challoner, D., Nature, 189, 1018–1019 (1961).
Randle, P. J., A. Rev. Physiol. 25, 291–324 (1963).
Opie, L. H., Nature, 227, 1055–1056 (1970).
Shug, A. L., and Shrago, E., J. Lab. clin. Med., 81, 214–217 (1973).
Braasch, W., Gudbjarnason, S., Puri, P. S., Ravens, K. G., and Bing, R. J., Circulation Res., 23, 429–438 (1968).
Wilkinson, J. H., and Robinson, J. M., Nature, 249, 662–663 (1974).
Weissler, A. M., Kruger, F. A., Baba, N., Scarpelli, D. C., Leighton, R. F., and Gallimore, J. K., J. clin. Invest., 47, 403–416 (1968).
Neely, J. R., Liebermeister, H., Battersby, E. J., and Morgan, H. E. Am. J. Physiol., 212, 804–814 (1967).
Kannengiesser, G. J., Lubbe, W. F., and Opie, L. H., J. molec. cell. Cardiol. (in the press).
Wroblewski, F., and La Due, J. S., Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. Med., 90, 210–213 (1955).
Spector, A., Progr. biochem. Pharmacol., 6, 130–176 (1971).
Hearse, D. J., Humphrey, S. M., and Chain, E. B., J. molec. cell. Cardiol., 5, 395–407 (1973).
Willebrands, A. F., ter Welle, H. F., and Tasseron, S. J. A., J. molec. cell. Cardiol., 5, 259–273 (1973).
Shell, W. E., Kjekshus, J. K., and Sobel, B. E., J. clin. Invest., 50, 2614–2625 (1971).
Shell, W. E., and Sobel, B. E., New Engl. J. Med., 291, 481–486 (1974).
Opie, L. H., Circulation, 45, 483–490 (1972).
Oliver, M. F., Circulation, 45, 491–500 (1972).
Wildenthal, K., Nature, 243, 226–227 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The erratum article can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1038/254460c0
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DE LEIRIS, J., OPIE, L. & LUBBE, W. Effects of free fatty acid and enzyme release in experimental glucose on myocardial infarction. Nature 253, 746–747 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/253746a0
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/253746a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Glucose–insulin–potassium therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2014)
-
Adverse effects of free fatty acid associated with increased oxidative stress in postischemic isolated rat hearts
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2006)
-
Substrate effects on sarcolemmal permeability in the normoxic and hypoxic perfused rat heart
Basic Research in Cardiology (1996)
-
Myocardial ischemia?Metabolic pathways and implications of increased glycolysis
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy (1990)
-
The role of fatty acids in ischemic tissue injury: difference between oleic and palmitic acid
Basic Research in Cardiology (1986)