Abstract
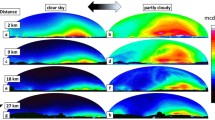
DURING the period of the International Quiet Sun Year, better opportunities may be found for the examination of airglow in the middle latitudes at a time when little or no auroral contamination is expected. With the view of measuring the intensities of the night airglow radiations emitted from the whole dome of the sky, a simple photoelectric type of photometer has been designed and built, in the Upper Atmosphere Research Section of the National Research Council, Ottawa, Canada.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park, F. R., J. Roy. Astron. Soc. Canad., 55, 203 (1961).
Roach, F. E., Ann. de Geophys., 17, 172 (1961) (and refs. 8–17 in this communication).
Kulkarni, P. V., and Chiplonkar, M. W., J. Poona Univ. (Sci.and Tech.), 18, 1 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KULKARNI, P. An All-Sky Photometer. Nature 196, 363–364 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/196363b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/196363b0
- Springer Nature Limited