Abstract
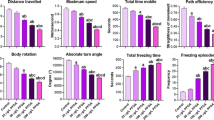
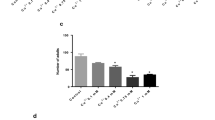
CYANIDE toxicity is closely associated with respiratory inhibition and, in many forms of life, death is attributed to disruption of oxidative metabolism through inhibition of the enzyme cytochrome oxidase. In insects also, cyanide inhibits the terminal oxidase, and it has been shown that in the insect heart cyanide sensitivity is closely associated with aerobic metabolism1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harvey, W. R., and Williams, C. M., Biol. Bull., 114, 23 (1958).
Paulet, G., Arch. intern. physiol. et biochim., 63, 340 (1955). Merker, H., Lockner, W., and Gerstenberg, E., Arch. Exp. Pathol. and Pharmacol., 232, 459 (1957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOND, E. Effect of Oxygen on Cyanide Poisoning in Insects. Nature 193, 1002–1003 (1962). https://doi.org/10.1038/1931002b0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/1931002b0
- Springer Nature Limited