Abstract
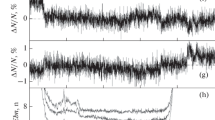
WHILE monitoring a remote continuous-wave station at the Ohio State University Radio Observatory, it has been found that large enhancements of signals often occur at the times of near approach of an artificial Earth satellite. The enhancements are of such magnitude as to indicate extensive ionization with scattering cross-section several orders of magnitude greater than the physical cross-section of the satellite1–3. In these observations it has been convenient to monitor the National Bureau of Standards time service station WWV near Washington, D.C., at a distance of 330 miles from Columbus. This communication describes some additional observations of the phenomenon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraus, J. D., Proc. Inst. Rad. Eng., 46, 611 (1958).
Kraus, J. D., Higgy, R. C., and Albus, J. S., Proc. Inst. Rad. Eng., 46, 1534 (1958).
Kraus, J. D., and Dreese, E. E., Proc. Inst. Rad. Eng., 46, 1580 (1958).
Kraus, J. D., Nature, 184, 669 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KRAUS, J., HIGGY, R., SCHEER, D. et al. Observations of Ionization induced by Artificial Earth Satellites. Nature 185, 520–521 (1960). https://doi.org/10.1038/185520a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/185520a0
- Springer Nature Limited