Abstract
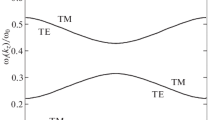
IN a recent paper1, the frequency of the principal lattice oscillation of an alkali halide crystal, in which the lattice of the alkali ions oscillates with respect to the lattice of the halide ions, was calculated on the basis of the simple Born model. It was found that the electric polarization of the crystal that accompanies this oscillation leads to a polarization field of the Lorentz type which tends to increase the relative displacement of the two lattices and has thus a marked influence on the principal frequency. Microscopically, this polarization may be regarded as due to small dipoles located at the lattice points. Because of the small amplitude of the oscillation, these dipoles will be practically point-dipoles, and since they are also cubically arranged, the polarization field will have just the Lorentz value, namely, 4π/3 times the polarization per unit volume. (Indeed, this appears to be the only case where the conditions postulated by Lorentz for obtaining the factor 4π/3 are rigorously satisfied.)
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Proc. Roy. Soc., A, 207, 447 (1951).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
KRISHNAN, K., ROY, S. Polarization Field and the Acoustic Modes of Oscillation of Alkali Halide Crystals. Nature 170, 159–160 (1952). https://doi.org/10.1038/170159a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/170159a0
- Springer Nature Limited