Abstract
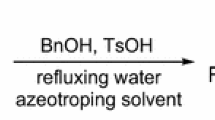
AN exception to the general applicability of the method devised by du Vigneaud and Meyer1 for the racemization of N-acyl-α-amino-acids has been discovered in the course of an attempt to racemize N-acetyl- and N-benzoyl-L-aspartic acids. The method of du Vigneaud and Meyer depends for its success upon the intermediate formation of a readily racemizable oxazolone when an aqueous solution of the sodium salt of such an acid is stirred with acetic anhydride. This treatment, which leads to the complete racemization of the N-acetyl derivatives of optically active methionine, cystine, arginine, tyrosine, phenylalanine, tryptophane and glutamic acid1,2, achieves, however, only 13 per cent and 24 per cent racemization when applied to N-acetyl- and N-benzoyl-L-aspartic acids respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
du Vigneaud, V., and Meyer, C. E., J. Biol. Chem., 98, 295 (1932).
du Vigneaud, V., and Sealock, R. R., J. Biol. Chem., 96, 511 (1932).
Baker, W., and Ollis, W. D., J. Chem. Soc., 345 (1949).
Harington, C. R., and Overhoff, J., Biochem. J., 27, 338 (1933).
Carter, H. E., and Stevens, C. M., J. Biol. Chem., 133, 117 (1940).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BARKER, C. Racemization of N-Acylaspartic Acids. Nature 168, 908–909 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1038/168908a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/168908a0
- Springer Nature Limited
This article is cited by
-
Anhydrides of N-Acylaspartic and N-Acylglutamic Acids
Nature (1952)