Abstract
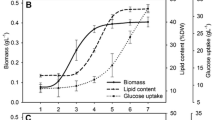
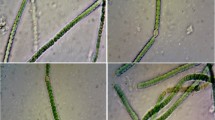
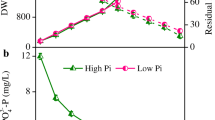
An analysis of lipid fatty acid composition in several unicellular and filamentous forms of mesophilic and thermophilic cyanobacteria was performed. At 47°C (the temperature of thermophilic cyanobacteria maintenance in the collection), the unicellular thermophilic Synechococcus strains were devoid of polyenoic acids as distinct from the mesophilic forms of this genus at the temperature of 20°C (the temperature of this cyanobacterial maintenance in the collection). In the thermophilic Synechococcus elongatusIPPAS B-267 strain, a decrease in temperature did not result in the occurrence of C18 polyenoic acids, but the quantitative relationship between the saturated and unsaturated fatty acids (S/U ratio) was decreased twofold. In contrast, the culturing of mesophilic strains at 25–32°C resulted in an increase in the S/U ratio due to an increase in the proportion of the 16:0 acid. In the Synechococcus IPPAS B-434 strain, this treatment resulted in a decrease in the relative content of monoenoic, mainly hexadecenoic, acids. The cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus, which lacks thylakoids, and whose photosystems are formed in a cell membrane, contained polyenoic acids. The filamentous thermophilic cyanobacterium Phormidium laminosum, at the maintenance temperature of 47°C, did contain polyenoic acids, but their proportion was considerably lower than that in the filamentous mesophilic forms, such as Tolypothrix sp. and Spirulina platensis. A relative content of hexadecenoic acids in Ph. laminosum was higher than in the mesophilic forms. A possible role of hexadecenoic acids in the processes of adaptation of cyanobacteria to high temperatures is discussed. A relationship between the characteristics of fatty acid composition fixed by evolution and the changes caused by adaptation to a particular environment is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Kenyon, C.N., Fatty Acid Composition of Unicellular Strains of Blue-Green Algae, J. Bacteriol., 1972, vol. 109, pp. 827-834.
Murata, N., Wada, H., and Gombos, Z., Modes of Fatty Acid Desaturation in Cyanobacteria, Plant Cell Physiol., 1993, vol. 33, pp. 933-941.
Cohen, Z., Margheri, M.C., and Tomaselli, L., Chemotaxonomy of Cyanobacteria, Phytochemistry, 1995, vol. 40, pp. 1155-1158.
Wood, B.G.B., Fatty Acids and Saponifiable Lipids, Algal Physiology and Biochemistry, Ch. 8, Stewart, W. et al., Eds., Oxford: Blackwell, 1974, pp. 236-265.
Sud'ina, E.G. and Lozovaya, G.I., Osnovy evolyutsionnoi biokhimii rastenii (The Basic Biochemistry of Plant Evolution), Kiev: Naukova Dumka, 1982.
Vargas, M.A., Rodriguez, H., Moreno, J., Olivares, H., Delcampo, J.A., Rivas, J., and Guerrero, M.G., Biochemical Composition and Fatty Acid Content of Filamentous Nitrogen-Fixing Cyanobacteria, J. Phycol., 1998, vol. 34, pp. 812-817.
Los, D.A., Fatty Acid Desaturases: Adaptive Expression and Principles of Regulation, Fiziol. Rast. (Moscow), 1997, vol. 44, pp. 528-540 (Russ. J. Plant Physiol., Engl. Transl.).
Katalog kul'tur mikrovodoroslei v kollektsiyakh SSSR (Catalogue of Microalgal Cultures in the Collection of USSR), Semenenko, V.E., Ed., Pushchino, 1991.
Vladimirova, M.G. and Semenenko, V.E., Intensivnaya kul'tura odnokletochnykh vodoroslei (Intense Culture of Unicellular Algae), Moscow: Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1962.
Klyachko-Gurvich, G.L., Semenova, A.N., and Semenenko, V.E., Lipid Metabolism of the Chloroplasts during Adaptation of Chlorella Cells to Lowering of Illumination, Fiziol. Rast. (Moscow), 1980, vol. 27, pp. 370-379 (Sov. Plant Physiol., Engl. Transl.).
Mouradian, E.A., Klyachko-Gurvich, G.L., and Pronina, N.A., Lipid Metabolism of Spirulina platensis under CO2-Stress, Advances in Plant Lipid Research Sanchez, J., et al., Eds., Sevilla: Univ. Sevilla, 1998, pp. 511-513.
Kiseleva, L.L., Horvath, I., Vigh, L., and Los, D.A., Temperature-Induced Specific Lipid Desaturation in the Thermophilic Cyanobacterium Synechococcus vulcanus, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1999, vol. 175, pp. 179-183.
Matsunaga, T., Takeyama, H., Miura, Y., Yamazaki, T., Furuya, H., and Sode, K., Screening of Marine Cyanobacteria for High Palmitoleic Acid Production, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1995, vol. 133, pp. 137-141.
Rippka, R., Waterbury, J., and Cohen-Bazire, G., A Cyanobacterium Which Lacks Thylakoids, Arch. Microbiol., 1974, vol. 100, pp. 419-436.
Selstam, E. and Campbell, D., Membrane Lipid Composition of the Unusual Cyanobacterium Gloeobacter violaceus sp. PCC 7421, Which Lacks Sulfoquinovosyl Diacylglycerol, Arch. Microbiol., 1996, vol. 166, pp. 132-135.
Sato, N. and Murata, N., Studies on the Temperature Shift Induced Desaturation of Fatty Acids in Monogalactosyldiacylglycerol in the Blue-Green Alga (Cyanobacterium) Anabaena variabilis, Plant Cell Physiol., 1981, vol. 22, pp. 1043-1050.
Li, R.H. and Watanabe, M.M., Fatty Acid Profiles and Their Taxonomy in Planktonic Species of Anabaena (Cyanobacteria) with Straight Trichomes, Phytochemistry, 2001, vol. 57, pp. 727-731.
Tomitani, A., Orada, K., Miyashita, H., Matthijsi, H.C.P., Ohno, T., and Tanaka, A., Chlorophyll b and Phycobilins in the Common Ancestor of Cyanobacteria and Chloroplasts, Nature, 1999, vol. 400, pp. 159-162.
Pinevich, A.V., Velichko, N.V., and Bazanova, A.V., Prochlorophytes Twenty Years On, Fiziol. Rast. (Moscow), 2000, vol. 47, pp. 730-734 (Russ. J. Plant Physiol., Engl. Transl.).
Henderson, R.J., Millar, R.M., Sargent, J.R., and Jostensen, J.P., Trans Monoenoic and Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids in Phospholipids of a Vibrio Species of Bacterium in Relation to Growth Conditions, Lipids, 1993, vol. 28, pp. 389-396.
Kiseleva, L.L., Horvath, I., Vigh, L., Lyukevich, A.A., and Los, D.A., Expression of the Gene for the Δ9 Acyl-Lipid Desaturase in the Thermophilic Cyanobacterium, J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2000, vol. 2, pp. 331-338.
Nakamura, Y., Kaneko, T., Sato, S., Ikeuchi, M., Katoh, H., Sasamoto, S., Watanabe, A., Iriguchi, M., Kawashima, K., Kimura, T., Kishida, Y., Kiyokawa, C., Kohara, M., Matsumoto, M., Matsuno, A., Nakazaki, N., Shimpo, S., Sugimoto, M., Takeuchi, C., Yamada, M., and Tabata, S., Complete Genome Structure of the Thermophilic Cyanobacterium Thermosynechococcus elongatus Strain BP-1, DNA Res., 2002, vol. 9, pp. 123-130.
Sallal, A.-K., Ghannoum, M.A., Al-Hasan, R.-H., Nimer, N.A., and Radwan, S.S., Lanosterol and Diacylglycerophosphocholines in Lipids from Whole Cells and Thylakoids of the Cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis fritschii, Arch. Microbiol., 1987, vol. 148, pp. 1-7.
Porankiewicz, J., Selstam, E., Campbell, D., and Oquist, G., Composition and Restoration of Photosynthesis during Low-Temperature Acclimation in Synechococcus sp. Strain PCC-7942, Physiol. Plant., 1998, vol. 104, pp. 405-412.
Klyachko-Gurvich, G.L., Tsoglin, L.N., Doucha, J., Kopetskii, J., Shebalina (Ryabykh), I.B., and Semenenko, V.E., Desaturation of Fatty Acids as an Adaptive Response to Shifts in Light Intensity, Physiol. Plant., 1999, vol. 107, pp. 240-249.
Honda, D., Yokota, A., and Sugiyama, J., Detection of 7 Major Evolutionary Lineages in Cyanobacteria Based on the 16S Ribosomal-RNA Gene Sequence-Analysis with New Sequences of 5 Marine Synechococcus Strains, J. Mol. Evol., 1999, vol. 48, pp. 723-739.
Miller, S.R. and Castenholz, R.W., Evolution of Thermotolerance in Hot-Spring Cyanobacteria of the Genus Synechococcus, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, pp. 4222-4229.
Robertson, B.R., Tezuka, N., and Watanabe, M.M., Phylogenetic Analyses of Synechococcus Strains (Cyanobacteria) Using Sequences of 16S rDNA and Part of the Phycocyanin Operon Reveal Multiple Evolutionary Lines and Reflect Phycobilin Content, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2001, vol. 51, pp. 861-871.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maslova, I.P., Mouradyan, E.A., Lapina, S.S. et al. Lipid Fatty Acid Composition and Thermophilicity of Cyanobacteria. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 51, 353–360 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUPP.0000028681.40671.8d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUPP.0000028681.40671.8d