Abstract
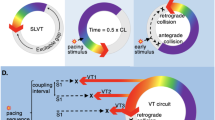
Atrial fibrillation (AF), atrial flutter and atrial tachycardia (AT) occur frequently in patients following implantation of an implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) for the treatment of ventricular tachyarrhythmias. Some new generation ICDs have incorporated atrial antitachycardia pacing therapy (ATP) and atrial pacing algorithms designed specifically for the prevention of AF. In the GEM III AT clinical evaluation, atrial ATP efficacy for termination of AF and AT was assessed. Overall ATP efficacy for AF/AT, based on device classification, was 40% when adjusted using the Generalized Estimating Equations to account for correlated data that arises from utilizing multiple episodes in some patients. However, many episodes of AF/AT were noted to terminate within 10 minutes of onset. Applying a more conservative definition of efficacy, termination within 20 sec of delivery of the last atrial ATP, efficacy for termination of AF/AT was 26%. 50 Hz burst pacing was shown to have minimal efficacy for termination of AF and modest incremental benefit following ramp or burst pacing therapies for AT. These observations provide a more realistic expectation of the value of atrial ATP in the ICD population with AF. Atrial ATP terminates some episodes of AT but previously reported efficacy rates of 40–50% are exaggerated and in part reflect spontaneous terminations of some AF/AT episodes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schoels W, Swerdlow CD, Jung W, Stein KM, Seidl K, Haffajee CJ. Worldwide clinical experience with a new dual-chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillator system. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2001;12:521–528.
Friedman PA, Dijkman B, Warman EN, Xia HA, Mehra R, Stanton MS, Hammill SC. Atrial therapies reduce atrial arrhythmia burden in defibrillator patients. Circulation 2001;104:1023–1028.
Adler SW 2nd, Wolpert C, Warman EN, Musley SK, Koehler JL, Euler DE. Efficacy of pacing therapies for treating atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with ventricular arrhythmias receiving a dual-chamber implantable cardioverter defibrillator. Circulation 2001;104:887–892.
IsraelCW, Hugl B, Unterberg C, Lawo T, Kennis I, Hettrick D, Hohnloser SH. Pace-termination and pacing for prevention of atrial tachyarrhythmias: Results from a multicenter study with an implantable device for atrial therapy. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2001;12:1121–1128.
Israel CW, Ehrlich JR, Gronefeld G, Klesius A, Lawo T, Lemke B, Hohnloser SH. Prevalence, characteristics and clinical implications of regular atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with atrial fibrillation: insights from a study using a new implantable device. JAmColl Cardiol 2001;38:355–363.
Carlson MD, John IP, Messenger J, Beau S, Kalbfleisch S, Gervais P, Cameron DA, Duran A, Val-Mejias J, Mackall J, Gold M for the ADOPT-A Investigators. A new pacemaker algorithm for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: Results of the Atrial Dynamic Overdrive Pacing Trial (ADOPT). J Am Coll Cardiol (in press)
Gillis AM. Clinical trials of pacing for maintenance of sinus rhythm. J Int Cardiac Electrophys (in press)
Gillis AM, Unterberg-Buchwald C, Schmidinger H, Massimo S, Wolfe K, Kavaney DJ, Otterness MF, Hohnloser SH for the GEM III AT Worldwide Investigators. Safety and efficacy of advanced atrial pacing therapies for atrial tachyarrhythmias in patients with a new implantable dual chamber cardioverter-defibrillator. J Am Coll Cardiol 2002;40:1653–1659.
Zeger S, Liang KY, Albert PS. Models for longitudinal data: A generalized estimating equation approach. Biometrics 1988;44:1049–1060.
Lee Ma, Weachter R, Pollak S, Keremers MS, Naik AM, Silverman R, Tuzi J, Wang W, Johnson LJ, Euler DE for the ATTEST Investigators. The effect of atrial pacing therapies on atrial tachyarrhythmia burden and frequency: Results of a randomized trial in patients with bradycardia and atrial tachyarrhythmias
Konings KT, Kirchhof CJ, Smeets JR, Wellens HJ, Penn OC, Allessie MA. High-density mapping of electrically induced atrial fibrillation in humans. Circulation 1994;89:1665–1680.
Padeletti L, Purerfellner H, Adler S, Waller T, Harvey MN, Horvitz L, Mugglin A, Kempen K, Holbrook R, Hettrick D. Atrial septal lead placement and atrial pacing algorithms for prevention of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: ASPECT Study results. PACE 2002;24;687.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gillis, A.M. Atrial Pacing Therapies for Prevention of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Implantable Defibrillators. Card Electrophysiol Rev 7, 345–347 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEPR.0000023135.19859.6d
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CEPR.0000023135.19859.6d