Abstract
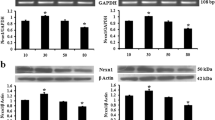
Age-dependent changes in the distribution of microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) were analyzed in young (3-months, N = 3) and old (24-months, N = 3) rat brain. In the young rats, MAP1 and MAP5 exhibited prominent immunostaining in the perikarya and dendrites whereas MAP2 was selectively localized in the dendrites. In the cerebellum, MAP2 was preferentially localized in finer and distal branches of Purkinje cell dendrites and in punctate deposits surrounding glomeruli. In general, aging resulted in obvious declines in MAP2- >> MAP1- and MAP5-immunoreactivities in the hippocampus and parietal cortex but no change in cerebellum. The results indicate that: (1) hippocampus is the most affected and cerebellum is the least affected region with regard to declines in MAPs-immunoreactivities in the aged rat brain; (2) dendrite-specific MAP2 is almost completely depleted from most dendrites in the hippocampus and cortex. In summary, loss of MAP2-immunoreactivity in the affected brain areas may be associated with age-related impairment of synaptic plasticity, cognition and memory functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Finch, C. E. 1993. Neuron atrophy during aging: programmed or sporadic? Trends Neurosci. 16:104–110.
Hasegawa, M., Arai, T., and Ihara, Y. 1990. Immunochemical evidence that fragments of phosphorylated MAP5 (MAP1B) are bound to neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease. Neuron 4(6):909–918.
Geddes, J. W., Lundgren, K., and Kim, Y. K. 1991. Aberrant localization of MAP5 immunoreactivity in the hippocampal formation in Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 30:183–191.
Olmsted, J. B. 1986. Microtubule associated proteins. Ann. Rev. Cell. Biol. 2:421–457.
Matus, A. 1988. Microtubule associated proteins: their potential role in determining neuronal morphology. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 11: 29–44.
Binder, L. I., Frankfurter, A., and Rebhun, L. I. 1986. Differential localization of MAP2 and tau in mammalian neurons in situ. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 466:145–166.
Caceres, A., Busciglio, J., Ferreira, A., and Steward, O. 1988. An immunocytochemical and biochemical study of the microtubule-associated protein MAP-2 during post-lesion dendritic remodeling in the central nervous system of adult rats. Mol. Brain Res. 3: 233–246.
Arnold, S. E., and Trojanowski, J. Q. 1996. Human fetal hippocampal development. 2. The neuronal cytoskeleton. J. Comp. Neurol. 367(2):293–307.
Kubanis, P., and Zornetzer, S. F. 1981. Age-related behavioural and neurobiological changes: A review with an emphasis on memory. Behav. Neural. Biol. 31:15–21.
Araki, T., Kato, H., Kanai, Y., and Kogure, K. 1994. Age-dependent changes in the second messenger and rolipram receptor systems in the gerbil brain. J. Neural Trans. 97:135–147.
Pagluisi, S. R., Gerrard, P., Abdallah, M., Talabot, D., and Catsicas, S. 1994. Age-related changes in expression of AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits: Is calcium permeability altered in hippocampal neurons? Neuroscience. 61:429–433.
Roth, G. S., Joseph, J. A., and Preston, M. R. 1995. Membrane alterations as causes of impaired signal transduction in Alzheimer's disease and aging. Trends Neurosci. 18:203–206.
Nicoletti, V. G., Condorelli, D. F., Dell'Albani, P., Ragusa, N., and Giuffrida Stella, A. M. 1995. AMPA-selective glutamate receptor subunits in the rat hippocampus during aging. J. Neurosci. Res. 40:220–224.
Paxinos, G., and Watson, C. 1982. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press, New York.
Chauhan, N. B., and Siegel, G. J. 1996. In situ analysis of Na,K-ATPase α-isoform mRNAs in aging rat hippocampus. J. Neurochem. 66(4):1742–1751.
Chauhan, N. B., and Siegel, G. J. 1997. Differential expression of Na,K-ATPase α-isoform mRNAs in aging rat cerebellum. Journal of Neuroscience Research. 47:287–299.
Chauhan, N. B., and Siegel, G. J. 1997. Na,K-ATPase: Increases in α1-mRNA and decreases in α3-mRNA levels in aging rat cerebral cortex. In press, Neuroscience.
Sternberger, L. A. 1979. Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edition, Wiley, New York.
Masliah, E., Mallory, M., Ge, N., Alford, M., Veinbergs, I., and Roses, A. D. 1995. Neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of apoE-deficient mice. Exp. Neurol. 136(2):107–122.
Gazzaley, A. H., Siegel, S. J., Kordower, J. H., Mufson, E. J., and Morrison, J. H. 1996. Circuit-specific alterations of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit 1 in the dentate gyrus of aged monkeys. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci., USA. 93(7):3121–3125.
Matus, A., and Green, G. D. J. 1987. Age-related increase in a cathepsin D like protease that degrades brain microtubule-associated proteins. Biochemistry. 26:8083–8086.
Leterrier, J. F., and Eyer, J. 1992. Age-dependent changes in the ultrastructure and in the molecular composition of rat brain microtubules. J. Neurochem. 59(3):1126–1137.
Neuman, K., Soosaar, A., Nornes, H. O., and Neuman, T. 1995. Orphan receptor COUP-TF I antagonizes retinoic-acid induced neuronal differentiation. J. Neurosci. Res. 41(1):39–48.
Tsui, C. C., Copeland, N. G., Gilbert, D. J., Jenkins, N. A., Barnes, C., and Worley, P. F. 1996. NARP, a novel member of the pentraxin family, promotes neurite outgrowth and is dynamically regulated by neuronal activity. J. Neurosci. 16(3): 2463–2478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chauhan, N., Siegel, G. Age-Dependent Organotypic Expression of Microtubule-Associated Proteins (MAP1, MAP2, and MAP5) in Rat Brain. Neurochem Res 22, 713–719 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027306227402
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027306227402