Abstract
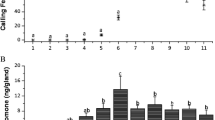
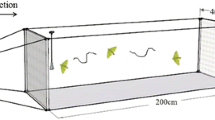
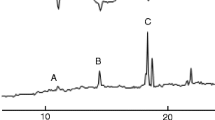
The female sex pheromone of Rhizoglyphus robini Claparède (Astigmata: Acaridae) was identified as α-acaridial [2(E)-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)- butenedial], which stimulated males sexually and enhanced the frequency of male mounting behavior. Although a hexane extract of females manifested alarm pheromone activity against tested males due to the presence of the alarm pheromone neryl formate, silica gel column fractions containing α-acaridial evoked increased mounting behavior by males at a dose of 0.1 female equivalent. Synthetic α-acaridial at a dose of 10 ng showed a peak of activity as a sex pheromone, with a convex dose–response relationship. Its content was determined to be 388 ± 244 ng per female and 163 ± 97 ng per male by GC. This is the first time that two pheromones (the alarm pheromone neryl formate, and the sex pheromone α-acaridial) have been demonstrated to be components of the same opisthonotal gland secretion in astigmatid mites. A mechanism for the appropriate expression of the two pheromones by the mites under different conditions is proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama, M., Sakata, T., Mori, N., Kato, T., Amano, H., and Kuwahara, Y. 1997. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, XLVI. Neryl formate, the alarm pheromone of Rhizoglyphus setosus Manson (Acarina: Acaridae) and the common pheromone component among four Rhizoglyphus mites. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 32:75–79.
Kuwahara, Y. 1999a. Chemical ecology in astigmatid mites, pp. 380–393, in T. Hidaka, Y. Matsumoto, K. Honda, H. Honda, and S. Tatsuki (Eds.). Environmental Entomology: Behavior, Physiology and Chemical Ecology. University of Tokyo Press, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Kuwahara, Y. 1999b. Rearing of astigmatid mites by culture medium. J. Acarol. Soc. Jpn 8:58–59 (in Japanese)
Kuwahara, Y., Asami, N., Morr, M., Matsuyama, S., and T. Suzuki. 1994. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, XXXVIII. Aggregation pheromone and kairomone activity of lardolure and its analogues against Lardoglyphus konoi and Carpoglyphus lactis. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 29:253–257.
Kuwahara, Y., Fukami, H., Ishii, S., Matsumoto, K., and Wada, Y. 1979. Pheromone study on acarid mites, II. Presence of the alarm pheromone in the mold mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank)(Acarina: Acaridae) and the site of its production. Jap. J. Sanit. Zool. 30:309–314.
Kuwahara, Y., Ishii, S., and Fukami, H. 1975. Neryl formate: Alarm pheromone of the cheese mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Schrank)(Acarina: Acaridae). Experientia 31:1115–1116.
Kuwahara, Y., Matsumoto, K., and Wada, Y. 1980. Pheromone study on acarid mite, IV. Citral: Composition and function as an alarm pheromone and its secretory gland in four species of acarid mites. Jap. J. Sanit. Zool. 31:73–80.
Kuwahara, Y., Sato, M., Koshii, T., and Suzuki, T. 1992. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, XXXII. 2-Hydroxy-6-methylbenzaldehyde, the sex pheromone of the brown-legged grain mite, Aleuroglyphus ovatus (Troupeau)(Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 27:253–260.
Kuwahara, Y., Shibata, C., Akimoto, K., Kuwahara, M., and Suzuki, T. 1988. Pheromone study on acarid mites, XIII. Identification of neryl formate as an alarm pheromone from the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini (Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 23:76–80.
Kuwahara, M., Takai, M., and Fujimoto, K. 1985. Simple rearing of the bulb mite, Rhizoglyphus robini and test methods of acaricides. Shokubutsu-boueki 39:68–70 (in Japanese)
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., Nakano, Y., Nakao, H., and Suzuki, T. 1989a. 2(E)-(4-Methyl-3-pentenyl)-butenedial, α-acaridial, a novel monoterpene from the acarid mite Tyrophagus perniciosus (Acarina, Acaridae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 53:1193–1196.
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., and Suzuki, T. 1989b. 2(E)-(4-Methyl-3-pentenylidene)-butanedial, β-Acaridial: A new type of monoterpene from the mold mite, Tyrophagus putrescentiae (Acarina, Acaridae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 53:875–878.
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., and Suzuki, T. 1990a. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, XXVII. Robinal, a highly conjugated monoterpenoid from the mite, Rhizoglyphus robini. Naturwissenschaften 77:387–388.
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., and Suzuki, T. 1990b. Hexyl 2-formyl-3-hydroxybenzoate, a fungitoxic cuticular constituent of the bulb mite Rhizoglyphus robini. Agric. Biol. Chem. 54:2593–2597.
Leal, W. S., Kuwahara, Y., Suzuki, T., and Kurosa, K. 1989c. Acaridial, the sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus polyphyllae. β-Pheromone study of acarid mites, XXI. Naturwissenschaften 76:332–333.
Mori, N. and Kuwahara, Y. 2000. Comparative studies of the ability of males to discriminate between sexes in Caloglyphus spp. J. Chem. Ecol. 26:1299–1309.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., and Kurosa, K. 1996. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites XLV. (2R,3R)-Epoxyneral: Sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus sp. (Acarina: Acaridae). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 1996:289–295.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., and Kurosa, K. 1998. Rosefuran: The sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus sp. J. Chem. Ecol. 24:1771–1779.
Mori, N., Kuwahara, Y., Kurosa, K., Nishida, R., and Fukushima, T. 1995. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, XLI. n-Undecane: The sex pheromone of the acarid mite Caloglyphus rodriguezi Samsinak (Acarina: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 30:415–423.
Nishimura K., Shimizu, N., Mori, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2002. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, LXIV. The alarm pheromone neral functions as an attractant in Schwiebea elongata (Banks) (Acari: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 37:13–18.
Ryono, A., Mori, N., Okabe, K., and Kuwahara, Y. 2001. Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites, LVIII. 2-Hydroxy-6-methylbenzaldehyde: Female sex pheromone of Cosmoglyphus hughesi Samsinak (Acari: Acaridae).Appl. Entomol. Zool. 36:77–81.
Sakata, T. and Kuwahara, Y. 2001. Structure elucidation and synthesis of 3-hydroxybenzene-1,2-dicarbaldehyde from astigmatid mites. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 65:2315–2317.
Sato, M., Kuwahara, Y., Matsuyama, S., Suzuki, T., Okamoto, M., and Matsumoto, K. 1993. Male and female sex pheromones produced by Acarus imobilis Griffiths (Acaridae: Acarina). Chemical ecology of astigmatid mites XXXIV. Naturwissenschaften 80:34–36.
Shimizu, N., Mori, N., and Kuwahara, Y. 2001. Aggregation pheromone activity of the female sex pheromone, β-acaridial, in Caloglyphus polyphyllae (Acari: Acaridae). Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 65:1724–1728.
Suzuki, T., Matsuyama, S., and Kuwahara, Y. 1992. A simple synthesis of α-acaridial. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 56:1888–1889.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizoguchi, A., Mori, N., Nishida, R. et al. α-Acaridial a Female Sex Pheromone from an Alarm Pheromone Emitting Mite Rhizoglyphus robini . J Chem Ecol 29, 1681–1690 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024235100289
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024235100289