Abstract
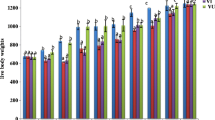
One hundred 6-week-old susceptible cockerels were inoculated with a pathogenic strain of infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) and kept in the same pen as 100 each of 6-week-old pullets, local chickens and broilers. The cockerels developed depression and diarrhoea on day 3 post inoculation (PI) and most of the pullets and some of the local chickens and broilers showed similar signs on day 4 PI. Loss in weight was severe and similar in the pullets and local chickens, being significantly greater than that in the broilers from days 3–11 PI. The total mortality was 85%, 66.7%, 30% and 20% for the pullets, cockerels, local chickens and broilers, respectively. The lesions were more severe in the pullets and local chickens than in the broilers. IBDV antigen and antibody were detected, respectively, in all the bursal and serum samples from the infected chickens tested. The contact exposure method used in this study simulates better what happens in nature than inoculation with IBDV. The reduced mortality observed among the local chickens, compared with that (61.5%) seen in earlier studies using intraocular inoculation of IBDV, may have been due to behavioural differences that tend to result in their ingesting a relatively low dose of the virus.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Akinokun, O., 1990. An evaluation of exotic and indigenous chickens as genetic materials for development of rural poultry production in Africa. In: E.B. Sonaiya (ed.), Rural Poultry in Africa, (African Network on Rural Policy Development, Ile-Ife), 56-61
Beard, C.W., 1989. Serologic procedures. In: H.G. Purchase, L.H. Arp, C.H. Domermuth and J.E. Pearson (eds), A Laboratory Manual for Isolation and Identification of Avian Pathogens, 3rd edn, (American Association of Avian Pathologists, Kenneth Square, PA), 192-200
Bumstead, N., Reece, R.L. and Cook, J.K.A., 1993. Genetic di¡erences in susceptibility of chicken lines to infectious bursal disease virus. Poultry Science, 72, 403-410
McNulty, M.S., 1989. Chicken anaemia agent. In: H.G. Purchase, L.H. Arp, C.H. Domermuth and J.E. Pearson (eds), A Laboratory Manual for Isolation and Identification of Avian Pathogens, 3rd edn, (American Association of Avian Pathologists, Kenneth Square, PA), 108-109
Okoye, J.O.A., 1984. Infectious bursal disease of chickens.Veterinary Bulletin, 54, 425-436
Okoye, J.O.A. and Aba-Adulugba, E.P., 1998. Comparative study of the resistance or susceptibility of local Nigerian and exotic chickens to infectious bursal disease. Avian Pathology, 27, 168-173
Okoye, J.O.A. and Uzoukwu, M., 1981. An outbreak of infectious bursal disease among chickens between 16 and 20 weeks old. Avian Diseases, 25, 1034
Reed, L.J. and Muench, H., 1938. A simple method of estimating 50% endpoints. American Journal of Hygiene, 27, 493-497
Salman, A., Shuaib, M.A., Suleiman, T.H. and Ginawi, M., 1983. Infectious bursal disease in the Sudan. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 15, 219-220
Steel, R.G.D. and Torrie, J.H., 1960. Principles and Procedures of Statistics, McGraw-Hall, New York)
Takase, K., Nonaka, F., Fukuda, T. and Yamada, S., 1982. Recovery of virus from faeces and tissues of chicks infected with cell culture adapted infectious bursal disease virus. Japanese Journal of Veterinary Science, 44, 207-211
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okoye, J., Aba-Adulugba, E., Ezeokonkwo, R. et al. Susceptibility of Local Nigerian and Exotic Chickens to Infectious Bursal Disease by Contact Exposure. Tropical Animal Health and Production 31, 75–81 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005159522203
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005159522203