Abstract
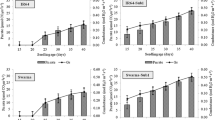
Seedling establishment of direct sown rice plants is less successful in flooded soil than in drained soil. This study was conducted to clarify the difference in morphogenesis of rice seeds sown in flooded and drained soils and to identify the morphological characteristics responsible for successful establishment of cultivars in flooded soil. Rice cultivars ASD1 and IR41996–50–2–1–3, superior in seedling establishment in flooded soil, and Mahsuri and IR72, non-superior (control), were sown at a depth of 25 mm in soil flooded with 25 mm of water or in drained soil. The coleoptile and 1st leaf emerged from the soil surface simultaneously in drained soil while in flooded soil the coleoptile emerged first. The coleoptile of superior cultivars, unlike the controls, elongated more in flooded soil than in drained soil. In flooded soil, the development of mesocotyl, 1st leaf, and roots were inhibited to a greater extent in the controls, than in the superior cultivars. In sealed flasks in which gas containing 0–21% O2 was exchanged daily, the superior cultivars developed longer coleoptiles than the controls at lower O2 concentrations. These findings suggest that the reason superior cultivars grow better in flooded soil than the controls is that the coleoptile elongates faster and longer in hypoxia and is able to reach the soil surface where O2 is available.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpi A and Beevers H 1983 Effect of O2 concentration on rice seedlings. Plant Physiol. 71, 30-34.
Atwell B J and Greenway H 1987 Carbohydrate metabolism of rice seedlings grown in oxygen deficient solution. J. Exp. Bot. 38, 466-478.
Avadhani P N, Greenway H, Lefroy R and Prior L 1978 Alcoholic fermentation and malate metabolism in rice germinating at low oxygen concentrations.Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 5, 15-25.
Bertani A, Brambilla I and Menegus F 1980 Effect of anaerobiosis on rice seedlings: growth, metabolic rate, and fate of fermentation products. J. Exp. Bot. 31, 325-331.
Chapman A L and Peterson ML 1962 The seedling establishment of rice under water in relation to temperature and dissolved oxygen. Crop Sci. 2, 391-395.
Chemical Society of Japan 1966 Handbook of Chemistry, Fundamental version II. Maruzen, Tokyo. pp 620-621 (In Japanese).
IRRI 1992 IRRISTAT user's manual. Version 92-1. IRRI, Manila.
Ishizawa K and Esashi Y 1984 Gaseous factors involved in the enhanced elongation of rice coleoptiles under water. Plant Cell Environ. 7, 239-245.
Jones J W 1933 Effect of reduced oxygen pressure on rice germination. J. Am. Soc. Agron. 25, 69-81.
Krishnasamy V and Seshu D V 1989 Seed germination rate and associated characters in rice. Crop Sci. 29, 904-908.
Ponnamperuma F N 1972 The chemistry of submerged soils. Adv. Agron. 24, 29-96.
Taylor D 1942 Influence of oxygen tension on respiration, fermentation, and growth in wheat and rice. Am. J. Bot. 29, 721-737.
Turner F T, Chen C-C and McCauley G N 1981 Morphological development of rice seedlings in water at controlled oxygen levels. Agron. J. 73, 566-570.
Vartapetian B B, Andreeva I N and Kursanova L 1974 Appearance of unusual mitochrondria in rice coleoptiles at conditions of secondary anoxia. Nature 248, 258-259.
Yamauchi M, Aguilar A M, Vaughan D A and Seshu D V 1993 Rice (Oryza sativaL.) germplasm suitable for direct sowing under flooded soil surface. Euphytica 67,177-184.
Yamauchi M and Chuong P V 1995 Rice seedling establishment as affected by cultivar, seed coating with calcium peroxide, sowing depth, and water level. Field Crops Res. 41, 123-134.
Yamauchi M, Herradura P S and Aguilar A M 1994 Genotype difference in rice postgermination growth under hypoxia. Plant Sci.100, 105-113.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamauchi, M., Biswas, J. Rice cultivar difference in seedling establishment in flooded soil. Plant and Soil 189, 145–153 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004250901931
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004250901931